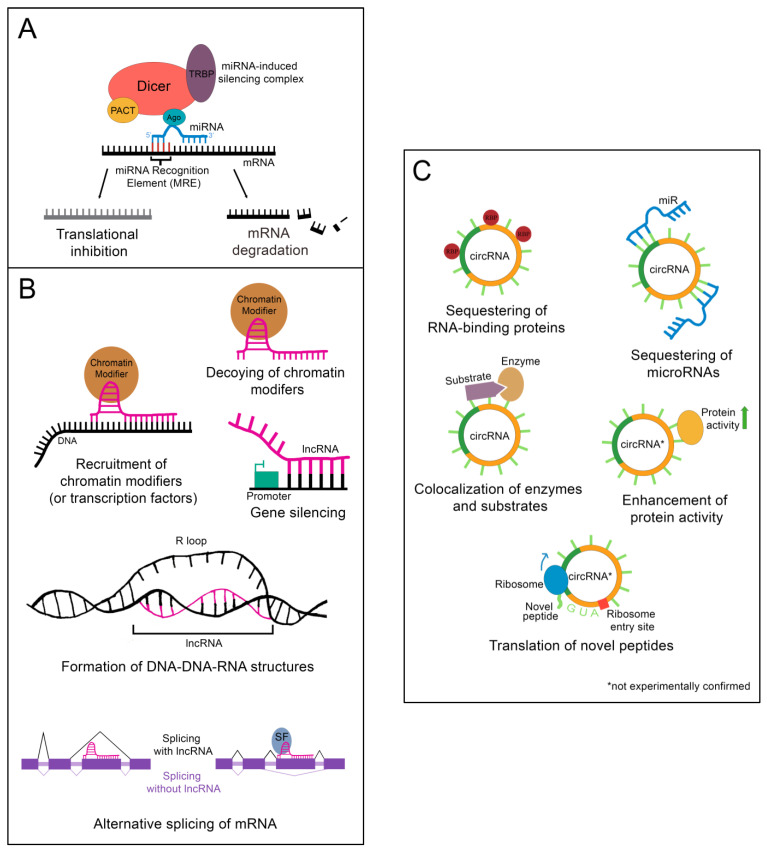
Figure 2.
Epigenetic regulation by ncRNAs. (A) The microRNA-induced silencing complex downregulates mRNAs through translational inhibition or degradation. TRBP: transactivation response element RNA-binding protein; PACT: protein kinase RNA activator; Ago: Argonaute (B) lncRNAs alter gene expression by binding DNA, binding mRNA, or by sequestering chromatin modifiers. DNA binding by lncRNAs can result in chromatin modifier or transcription factor recruitment, gene silencing, or the formation of DNA-DNA-RNA structures. Binding of a lncRNA to mRNA often leads to alternative splicing of the mRNA. For instance, the presence of a lncRNA on an exon can lead to that exon being skipped. Alternatively, recruitment of splicing factors by a bound lncRNA can lead to the retention of an exon that would otherwise be skipped. SF: splicing factor (C) CircRNAs function as sponges for RNA-binding proteins or microRNAs. Some can also colocalize enzymes with their substrates. A few are proposed to enhance protein activity or be translated into novel peptides, although these functions have yet to be experimentally validated. RBP: RNA-binding protein.