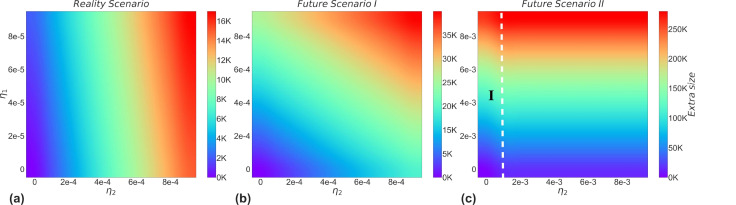
Fig. 8.
Effect of the rate of loss of cross-immunity on the extra size caused by strain 2. The extra size represents the number of infections added to the initial number of illnesses. (a), (b), and (c) show the impact of the rate of loss of cross-immunity on the competition between strains, i.e. the extra size of the outbreak caused by strain 2, in the real scenario as well as in the two possible future scenarios, respectively. Reality scenario: The size of the partial cross-immunity gained after recovery from infection with both strains is very different, and the protection gained is maintained for a longer period. Future scenario I: The difference in the size of the partial cross-immunity obtained after recovery from infection with both strains is not large and the protection obtained is maintained for a longer period. Future scenario II: The difference in the size of the partial cross-immunity obtained after recovery from infection with the two strains is small, but the protection obtained is maintained for a shorter period. The left side of the white dashed line shows that subplot (b) is part of it.