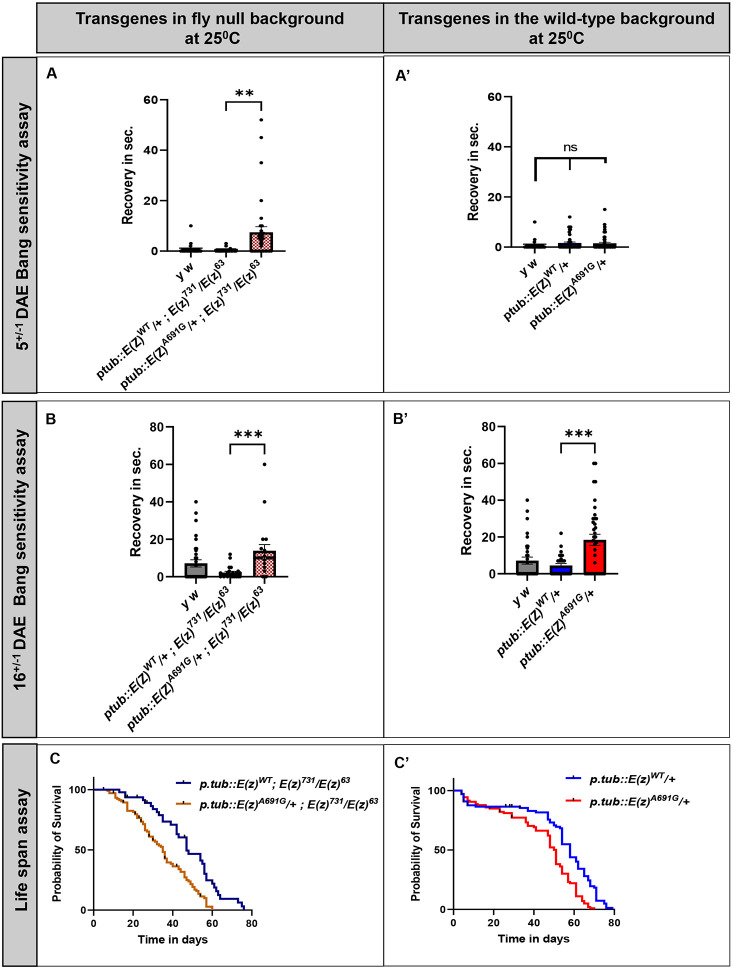
Figure 4: Behavior study with the transgenic flies.
A-A’: Bang sensitivity performed at 5 days after eclosion (DAE): ptub::E(z)A691G transgenic flies in the fly null background observed to be bang sensitive than ptub::E(z)WT(FIGURE 4A, p=0.0041). When similar experiment is carried out in the wild-type background ptub::E(z)A691G do not behave different than the wild-type ptub::E(z)WT(FIGURE 4A’, p=ns).
B-B’: Bang sensitivity performed at 16 DAE: ptub::E(z)A691G transgenic flies in the fly null background continues to show bang sensitivity at 16 DAE when compared to ptub::E(z)WT(FIGURE 4B, p=0.0004). In the wild-type background the ptub::E(z)A691G starts showing the bang sensitivity when compared to ptub::E(z)WT(FIGURE 4B’, p=0.0002).
C-C’: Life span assay : ptub::E(z)A691G transgenic flies in the fly null background live shorter than the ptub::E(z)WT(FIGURE 4C, Median Survival: E(z)WT = 47, E(z)A691G = 35, p<0.0001). However, in the fly wild-type background, ptub::E(z)A691G transgenic flies shows a similar trend in life span assay when compared to ptub::E(z)WT(FIGURE 4C’, Median Survival: E(z)WT = 58, E(z)A691G = 51, p<0.0001).
p-value were determined by unpaired t-tests.