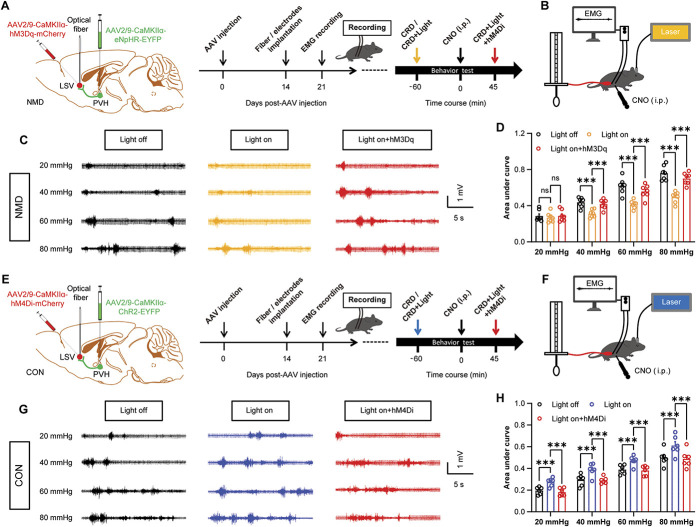
Figure 7.
Inhibition of PVH–LSV pathway reduces visceral hyperalgesia, whereas activation of PVH–LSV pathway contributes to adaptive visceral pain behavior. (A) Experimental procedure of a dual-virus strategy that specifically regulates the activity of CaMKIIα-positive neurons of the PVH–LSV pathway in NMD mice by combining optogenetic with chemogenetic (left) and schematic of experimental timelines for optogenetic and chemogenetic manipulation (right). (B) Schematic EMG recording for evaluating visceral pain under optogenetic and chemogenetic manipulation. (C) Representative EMG traces of NMD mice were recorded at 20, 40, 60, and 80 mm Hg, respectively. (D) The area under the curve of EMG at 20, 40, 60, and 80 mm Hg in NMD mice (F (3, 18) = 86.90, ***P < 0.001, two-way repeated-measure ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, n = 7 mice per group). (E) Experimental procedure of a dual-virus strategy that specifically regulates the activity of CaMKIIα-positive neurons of the PVH–LSV pathway in CON mice by combining optogenetic with chemogenetic (left) and schematic of experimental timelines for optogenetic and chemogenetic manipulation (right). (F) Schematic EMG recording for evaluating visceral pain after optogenetic and chemogenetic manipulation. (G) The representative EMG traces of CON mice were recorded at 20, 40, 60, and 80 mm Hg, respectively. (H) The area under the curve of EMG at 20, 40, 60, and 80 mm Hg in CON mice (F (3, 15) = 101.1, ***P < 0.001, two-way repeated-measure ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, n = 6 mice per group). n.s. indicates nonsignificant differences. P > 0.05. ANOVA, analysis of variance; CRD, colorectal distention; LSV, lateral septal ventral; NMD, neonatal maternal deprivation; PVH, paraventricular hypothalamic.