FIG 2.
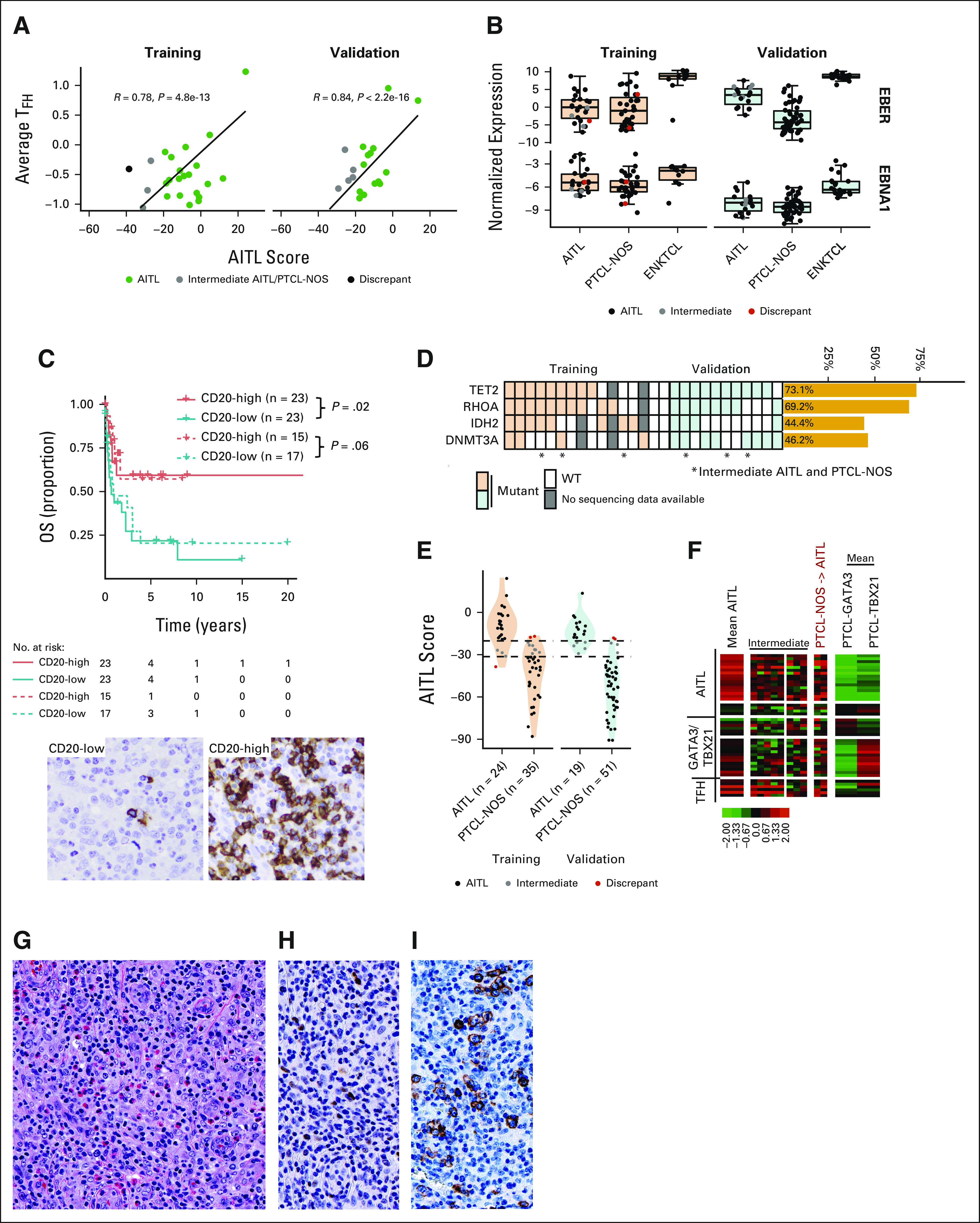
AITL classification. (A) Scatterplot of the AITL diagnostic score versus the average expression of five TFH-related genes in training and validation AITLs. (B) Boxplot of EBER and EBNA1 transcript expression in the AITLs (training/validation cohort). (C) Kaplan-Meier curve of OS of AITLs in the combined cohorts by CD20 mRNA expression. Solid lines are cases classified as AITL by molecular classification (P = .02); dotted lines are AITL by pathology (P = .06). CD20 expression in representative low- and high-expression AITL cases (400×). (D) Mutation status of cases with available sequencing data. Cases that were AITL-PTCL-NOS intermediate or did not classify as AITL on the NanoString classifier are noted with an asterisk. (E) Violin and dot plot of AITL classification diagnostic scores in AITL and PTCL-NOS cases profiled on the nCounter. Cases that were discordant between AITL and PTCL-NOS are given in red, and intermediate AITL cases in gray. (F) Heatmaps of AITL showing disagreement by NanoString classification in the validation cohort. The mean signature of the concordant cases is shown. For cases labeled intermediate, those diagnosed as AITL by consensus pathology review are on the left and intermediate cases diagnosed as PTCL-NOS are on the right. Two PTCL-NOS classified as AITL by nCounter. (G-I) Shown focal expression of BCL-6 and ICOS (400x; G, H, and I; G, H&E, H, BCL-6 and I, ICOS) seen in a PTCL-NOS case that was classified as AITL by the nCounter platform. AITL, angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma; BCL-6, B-cell lymphoma 6; ENKTCL, extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma; ICOS, inducible T cell co-stimulator; NOS, not otherwise specified; OS, overall survival; PTCL, peripheral T-cell lymphoma; TFH, T follicular helper; WT, wild type.
