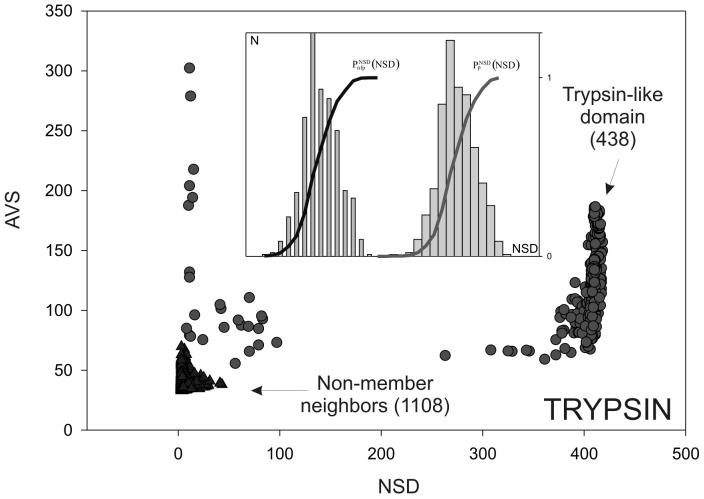
Figure 1.
An example of a domain sequence neighborhood (Trypsin-like domains). Each domain corresponds to one dot in the figure. NSD, number of similarities to the group (i.e. to trypsin domains); AVS, average of group similarities. The members of the group (‘self’) are shown as circles and domains that are not members but still have a significant (P < 1) similarity with the group (‘non-self’) are shown as triangles. (Inset) Schematic representation of the statistical parameters 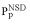 (•) and
(•) and 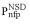 (•). Values of
(•). Values of 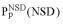 and
and 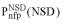 are simply read out from the precomputed empirical distributions. A similar procedure is followed for the AVS scores. The resulting six values are combined to calculate a probabilistic score (4) or used as the input parameters of artificial neural networks (5).
are simply read out from the precomputed empirical distributions. A similar procedure is followed for the AVS scores. The resulting six values are combined to calculate a probabilistic score (4) or used as the input parameters of artificial neural networks (5).