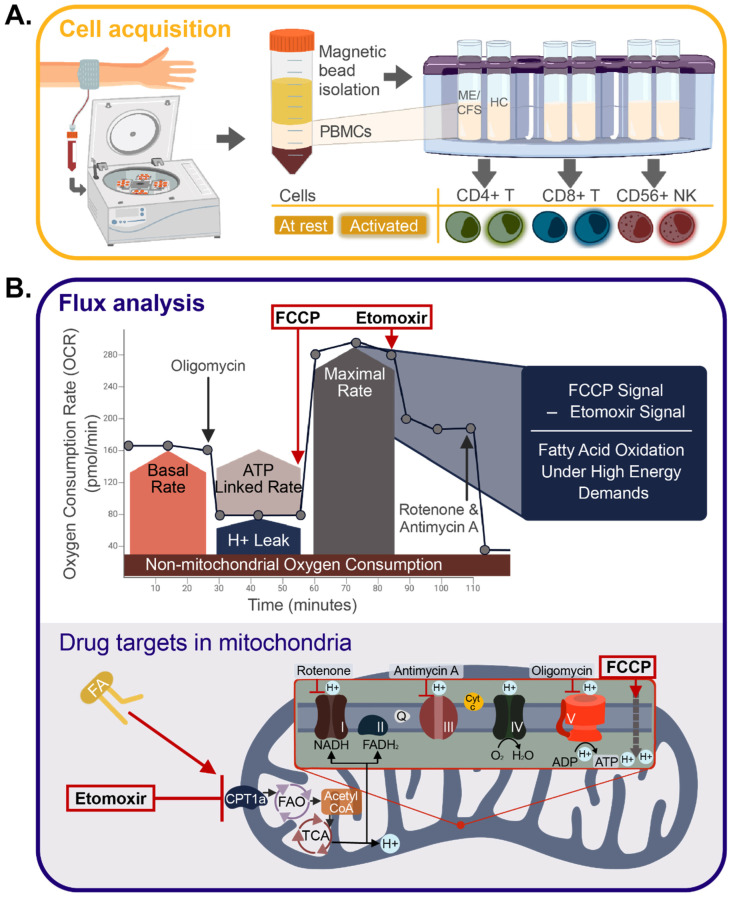
Figure 1.
Immune cell isolation study design and extracellular flux analysis. (A) Cell acquisition approach, where peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from whole blood taken from both healthy controls (HC) and individuals with ME/CFS. Magnetic bead isolation was performed using positive selection, starting with CD56+ Natural Killer (NK) cells, followed by CD8+ T cells, and, finally, CD4+ T cells. Isolated immune cells were activated 24 h before the experiment with ⍺CD3/⍺CD28 and IL2 for T cells and IL15/IL12 for NK cells. (B) Seahorse drug injection strategy, where the y-axis represents the rate of oxygen consumption in pmol/minutes, and the x-axis is the time during the assay in minutes. A modified Mito Stress test drug injection strategy was performed on isolated immune cell types. Etomoxir, an inhibitor of fatty acid oxidation, was included in post-FCCP measurements to calculate the fatty acid contribution of each cell type under high energy demands. Included in panel B is a visual representation of each drug target within the mitochondria (FA = fatty acid, FAO = fatty acid oxidation, TCA = tricarboxylic acid cycle).