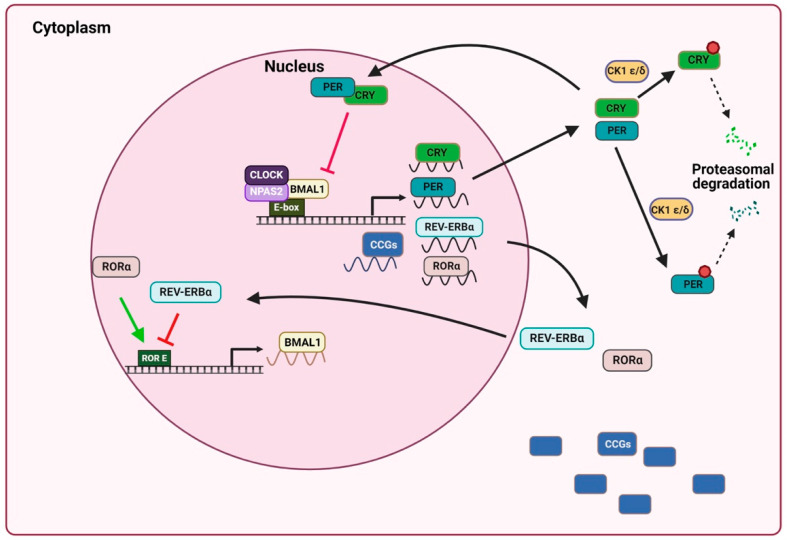
Figure 1.
Schematic model of mammalian circadian clock mechanism. The molecular clock is composed of interconnected transcription feedback loops: the transcription factors CLOCK/NPAS2 and BMAL1 produce a heterodimer that binds to the E-box in the promoter and activates the transcription of Per, Cry, Rev-erbα, Rorα and CCGs. CRY and PER dimerize and enter the nucleus, where CLOCK-BMAL1-activated transcription is inhibited, thus generating an oscillatory pattern of gene expression. In the cytoplasm, PER and CRY are phosphorylated by CK1 ε/δ for its degradation. The REV-ERBα receptor inhibits Bmal1 expression, while RORα positively regulates Bmal1 expression. Brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1 (Bmal1); cysteine kinase 1 ε/δ (CK1 ε/δ); circadian locomotor output cycles kaput (Clock); cryptochrome (Cry); neuronal PAS domain protein 2 (NPAS2); Period (Per); reverse strand of protein ERB alpha (Rev-erbα); orphan retinoic acid receptor-related alpha (RORα). Image created using BioRender.com (accessed on 22 November 2022).