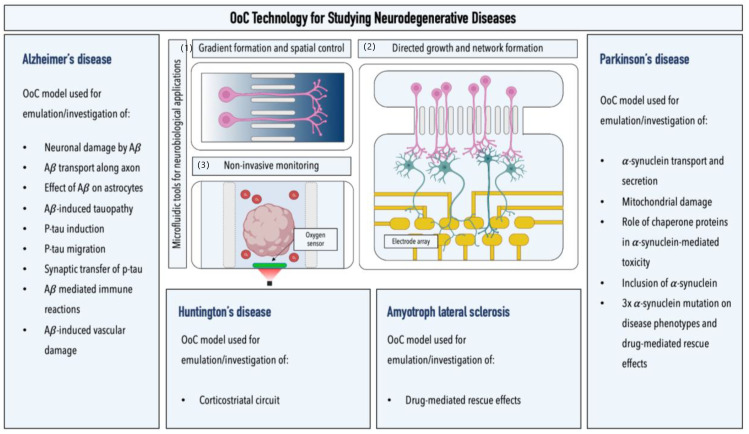
Figure 4.
Overview of microfluidic models for studying neurodegenerative diseases. Graphical illustrations highlight the advantages of microfluidic setups for studying neurodegenerative diseases: (1) generation of biochemical gradients (image illustrates two interconnected microfluidic channels with varying concentrations); (2) noninvasive monitoring of cells of the neurovascular unit by the integration of electrical, optical, and electrochemical sensors (image illustrates a brain organoid-on-a-chip platform equipped with integrated luminescent oxygen sensor spots for recording cellular respiration); and (3) directed growth and network formation (image illustrates two interconnected microfluidic chambers that allow for the directed growth and functional connection of two spatially separated neuronal populations; an integrated multielectrode array allows for the electrophysiological recording of neuronal activity in the downstream chamber of the device).