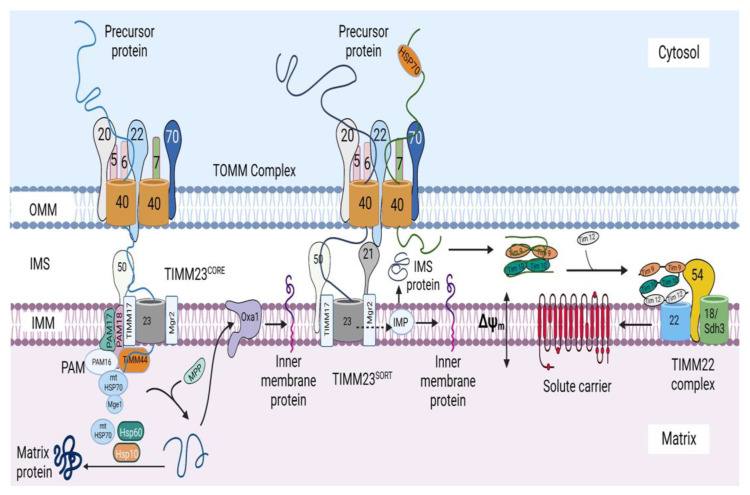
Figure 5.
Import of inner-mitochondrial membrane and matrix proteins. The presequence-carrying precursors are first recognized by TOMM20, which binds to them and transfers them to TOMM22, after which they are translocated through the TOMM40 channel, through which they enter the IMS, where they bind to the IMS domain of TOMM22. TIMM21 then binds the IMS domain of TOMM22, thereby promoting the dissociation of the precursors. Thereafter, TIMM50 binds to the precursor proteins and transfers the precursors into the TIMM23 channel. The Δψm exerts an electrophoretic effect on the positively charged N terminus of precursors and activates the TIMM23 channel, thereby aiding in the movement of the precursors through the TIMM23 channel. The hydrophobic sorting signals of the precursors are then recognized by Mgr2, which then binds to the sorting signals and controls the release of the precursors into the inner membrane. Subsequently, the inner-membrane peptidase (IMP) removes the hydrophobic sorting sequences, and the mature proteins are either released into the IMS or remain anchored in the inner membrane by an additional hydrophobic segment. Precursor proteins containing presequences devoid of hydrophobic sorting signals are destined for the matrix and are imported through the cooperation of the TOMM, TIMM23CORE, and PAM machineries. After translocation through the TOMM40 channel, these precursors bind to the IMS domain of TOMM22, after which TIMM50 binds these precursors and transfers them to the TIMM23 channel. TIMM44 then binds to the precursor as it emerges on the matrix side of the TIMM23 channel and transfers it to mtHsp70, which imports the protein into the matrix. The presequences are removed by the matrix processing peptidase (MMP), and the proteins are folded into their mature forms by the soluble form of mtHSP70 and the HSP60-HSP10 chaperonin complex. Oxa1 aids in the export of some of the transmembrane segments of some inner-membrane precursors from the matrix into the inner mitochondrial membrane. Following their synthesis in the cytosol, carrier precursors are bound to cytosolic chaperones of the Hsp70 and Hsp90 classes to prevent aggregation. Thereafter, these chaperones deliver the precursors to TOMM70, which then transfers this precursor to TOMM22, after which they are transferred to the TOMM40 channel and translocated across the OMM in a loop formation. The small TIM chaperones of the IMS are recruited to the channel exit by an N-terminal segment of the channel protein TOMM40. TIMM54, a subunit of the TIMM22 machinery, recruits the small TIMM chaperones to the TIMM22 complex, after which, the precursors are delivered to the TIMM22 channel. The Δψm activates the TIMM22 channel and exerts an electrophoretic effect on the carrier precursors, which aids in the movement of the precursors through the channel. Finally, the precursors are released laterally from the TIMM22 complex into the IMM. OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane, IMS, intermembrane space; Δψm, mitochondrial membrane potential. The figure was created with Biorender.com.