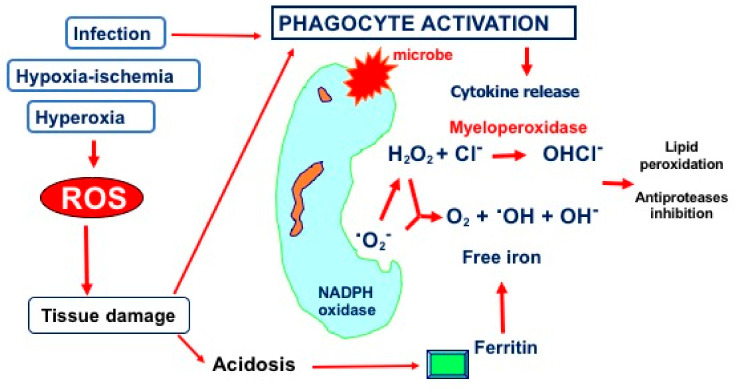
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of free radical generation during phagocyte activation. Following injury, due to infection, hypoxia–ischemia, or hyperoxia, neutrophils release ROS. The superoxide anion (·O2−), the most abundant radical species, is the first stage of bacterial killing reaction, which is followed by generation of other ROS, such as hydroxyl radical (·OH) by free irons and hypochlorous acid (OHCL−) by myeloperoxidases.