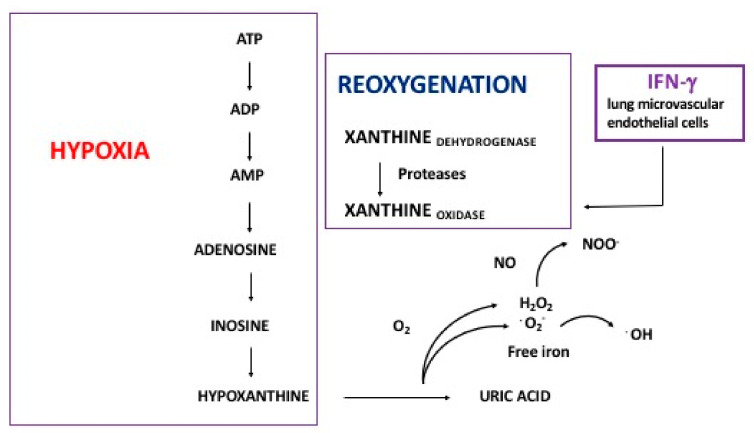
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of free radical generation during hypoxia–reoxygenation. Hypoxanthine derives from degradation of adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) during hypoxia-induced anaerobic metabolism. During reoxygenation, xanthine oxidoreductase catalyzes hydroxylation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and uric acid, inducing the release of ROS. Xanthine oxidoreductase exists in two forms: xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase. An irreversible proteolytic conversion of xanthine dehydrogenase to xanthine oxidase can also be specifically induced by IFN-γ in lung microvascular endothelial cells.