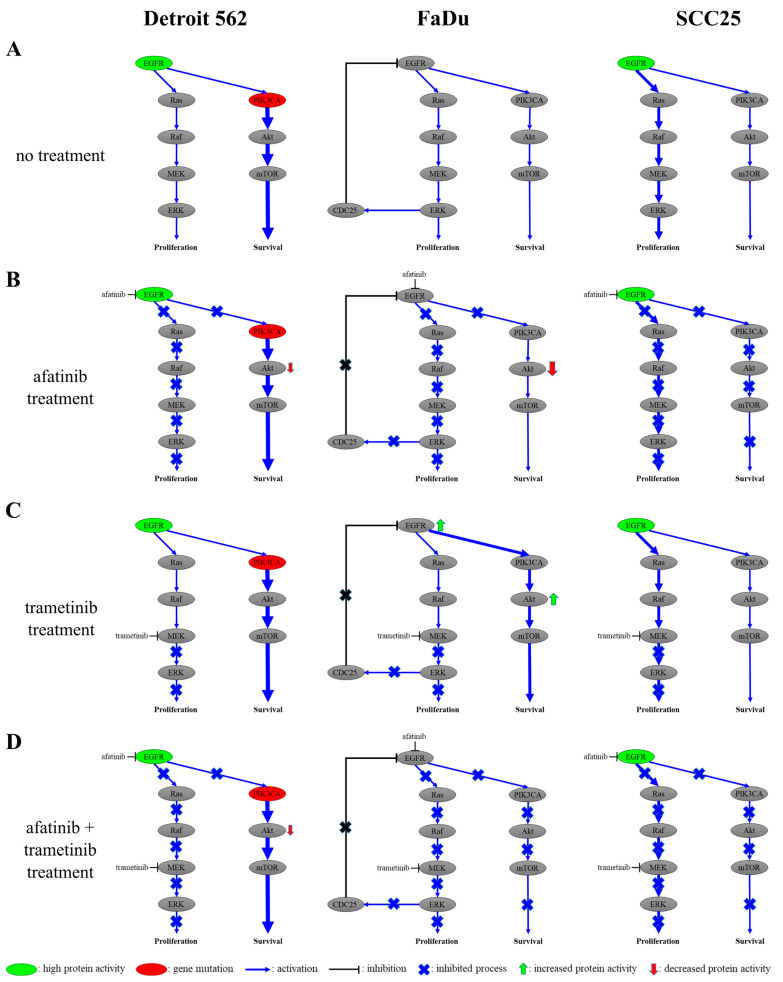
Figure 8.
Signaling models for in vitro head-and-neck-cancer-cell lines. These models are based on our protein-expression and -phosphorylation measurements and viability assays. (A) The EGFR-initiated signaling in untreated cells. The PI3K/Akt pathway is significant in Detroit 562 cells due to the PIK3CA mutation, the MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways are equally strong in FaDu cells and the MEK/ERK pathway is dominant in SCC25 cells. An ERK/CDC25/EGFR feedback loop is present in FaDu cells. (B) Signaling under afatinib treatment. Upon treatment with afatinib, the pathways of Detroit 562 and FaDu cells are partially inhibited, while those of SCC25 cells are completely inhibited. This is due to a mutation in Detroit 562 cells and the feedback in FaDu cells. (C) Signaling under trametinib treatment. Upon treatment with trametinib, the pathways of Detroit 562 and FaDu cells are partially inhibited, while those of SCC25 cells are completely inhibited. This is due to a mutation in Detroit 562 cells and the feedback in FaDu cells. (D) Signaling under afatinib + trametinib treatment. Upon treatment with afatinib + trametinib, the pathways of Detroit 562 cells are partially inhibited, while the pathways of FaDu and SCC25 cells are completely inhibited. This is due to the PI3K mutation in Detroit 562 cells.