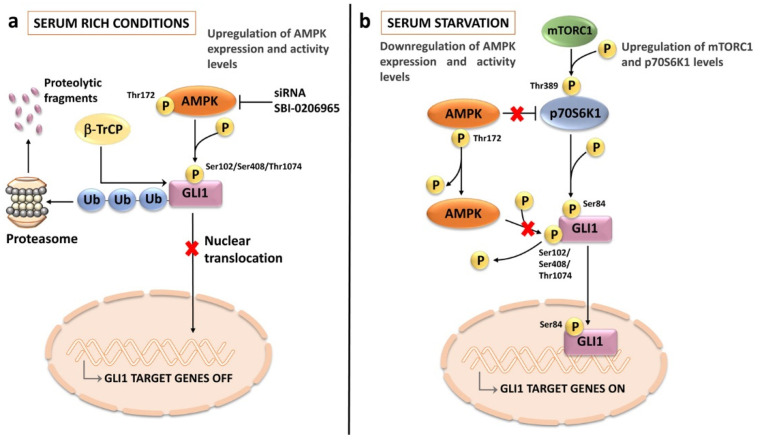
Figure 7.
Interactions between AMPK and HH signaling pathways in T-ALL cells: (a) under serum-rich conditions, AMPK is overexpressed and active (i.e., phosphorylated at Thr172). Active AMPK phosphorylates GLI1 at multiple amino acid residues. This phosphorylation leads to GLI1 ubiquitination by β-TrCP followed by proteasomal degradation; (b) when T-ALL cells are serum starved, AMPK expression and activity levels are downregulated, hence GLI1 is not phosphorylated at AMPK-dependent residues. In contrast, the mTORC1/p70S6K1 axis is overactive, due to AMPK inactivation/decreased expression. p70S6K1 kinase phosphorylates GLI1 at Ser84, thereby increasing the stability of GLI1 and enhancing its transcriptional activity. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; β-TrCP, β-transducin repeat containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase.