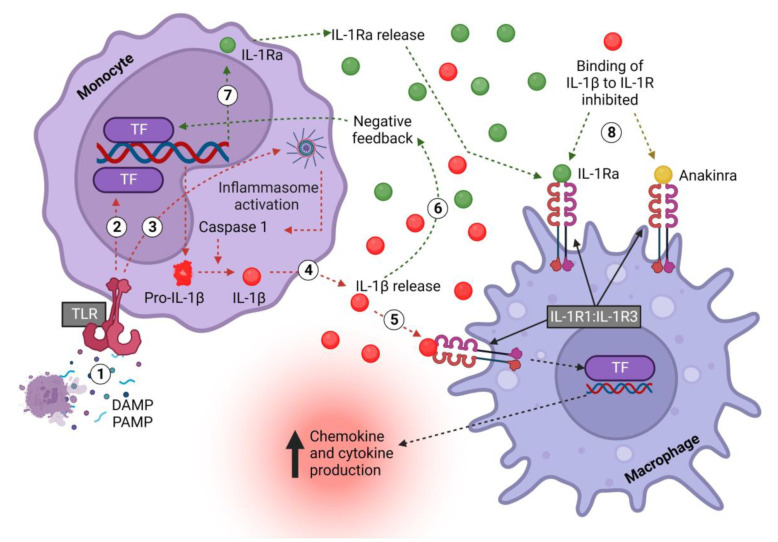
Figure 2.
Monocyte-derived IL-1β and IL-1Ra signaling pathway in macrophages. (1) DAMPS/PAMPS bind TLRs on monocytes and (2) activate downstream TFs, which induce the transcription of pro-IL-1β and release into the cell cytoplasm. (3) In monocytes, TLR signaling also induces the formation of inflammasomes, which activate caspase-1, which in turn cleaves pro-IL-1β, thus converting it into the mature and biologically active form. (4) Active IL-1β is released to (5) activate the IL-1R1:IL-1R3 receptor complex, thus exerting multiple, mostly pro-inflammatory effects, including inducing the transcription of chemokines to promote immune cell recruitment and cytokines to promote inflammation. (6) Concurrently, pro-inflammatory mediators, including IL-1β itself, (7) increase the production of IL-1Ra. (8) IL-1Ra is released and competitively inhibits the binding of IL-1 to IL-1R1. The drug anakinra acts in an identical fashion. IL—interleukin; Ra—receptor antagonist; DAMP—damage-associated molecular pattern; PAMP—pattern-associated molecular pattern; TLR—Toll-like receptor; R1—receptor 1; TF—transcription factor. Created with biorender.com.