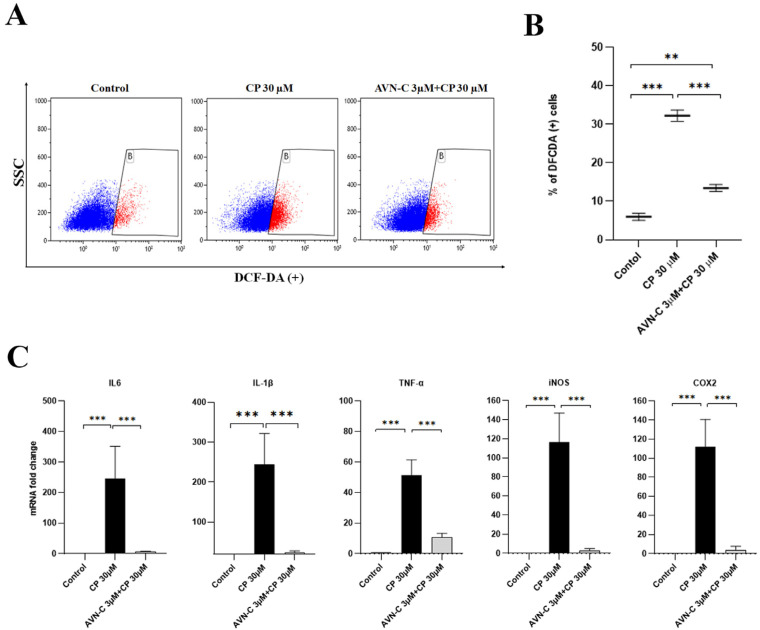
Figure 5.
AVN-C reduces apoptotic bodies in CP-induced ototoxicity in HEI-OC1 cells. (A,B) ROS significantly increased when 30 µm CP was administered to HEI-OC1 cells (*** p ≤ 0.001, Control vs. CP and AVN-C vs. CP; ** p ≤ 0.01, Control vs. AVN-C+CP ) and AVN-C mitigated CP cytotoxicity by protecting the HEI-OC1 cells against CP-induced damage (*** p ≤ 0.001; n = 3 each). Demarcated (B) area in red shows DCFDA positive. (C) The levels of inflammatory cytokines (IL6, IL-1β, TNF-α, iNOS, and COX2) that are known to trigger inflammation of auditory hair cell death were all upregulated in the CP-treated group (*** p ≤ 0.001, Control vs. CP), and AVN-C significantly downregulated the expression of these genes (*** p ≤ 0.001, AVN-C vs. CP; n = 3 each). One way-ANOVA was used and p ≤ 0.05 indicated significance.