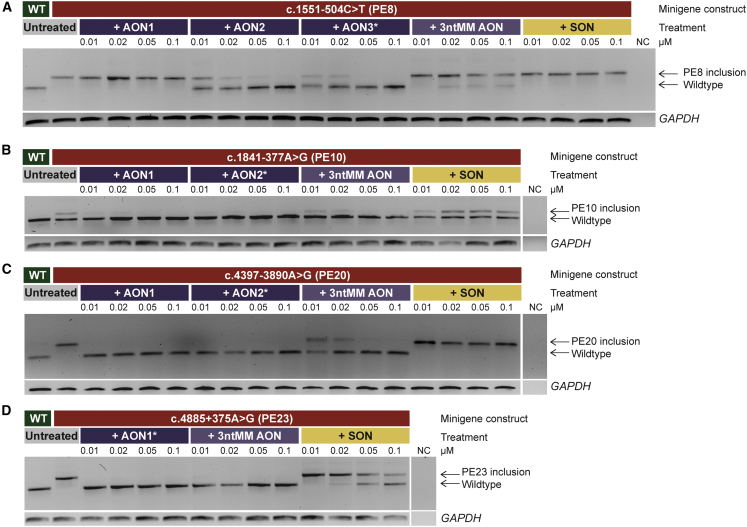
Figure 3.
Antisense oligonucleotide (AON) treatment dilution series for four deep-intronic targets
Representative gel images from AON treatment studies in minigenes.
(A) Two out of three AONs (AON2 and AON3) were effective in reverting a 118-nt pseudoexon (PE) inclusion in intron 8, caused by variant c.1551-504C>T, for all tested concentrations. A three-nucleotide mismatch antisense oligonucleotide (3ntMM AON) of the most potent AON (AON3, marked with an asterisk) and a scrambled oligonucleotide (SON), had minimal to no effect on reverting PE inclusion.
(B) Variant c.1841-377A>G resulted in partial inclusion of a 94-nt PE in intron 10. Both AONs efficiently reverted PE inclusion, while a 3ntMM AON of AON2 had reduced effect and an SON was not effective.
(C) Variant c.4397-3890A>G caused inclusion of an 87-nt PE in intron 20. Both AONs efficiently reverted PE inclusion, while a 3ntMM AON of AON2 had reduced effect and an SON was not effective.
(D) Variant c.4885+375A>G causes inclusion of a 130-nt PE in intron 23. The AON that could be designed for the region was efficient in reverting PE inclusion. A 3ntMM AON was fully effective as well and an SON had reduced effect. NC, negative control; nt, nucleotides; WT, wild type. Transfections were performed in duplicate, GAPDH was used as loading control in all experiments.