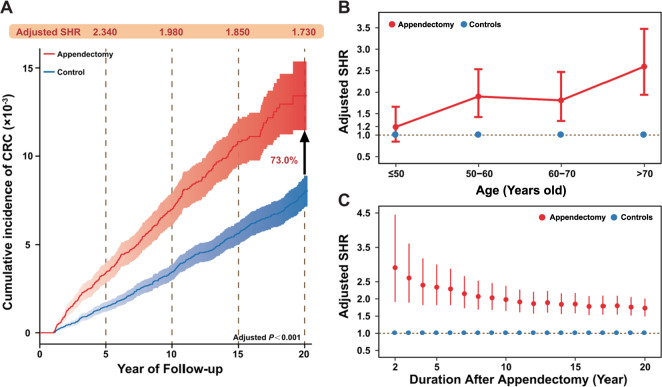
Fig. 1. The appendectomy increased the overall cumulative risk of colorectal cancer development based on the longitudinal epidemiological study on Hong Kong Cohort.
A The cumulative incidence of colorectal cancer (CRC) was increased by 73% in appendectomy cases compared with controls during the 20 years follow-up. B The adjusted sub-distribution hazard ratio (SHR) for CRC development stratified by age (≤50 years old, 50–60 years old, 60–70 years old, and >70 years old). C The temporal trends of the adjusted SHR for CRC development over the 20 follow-up years in appendectomy cases compared with controls.