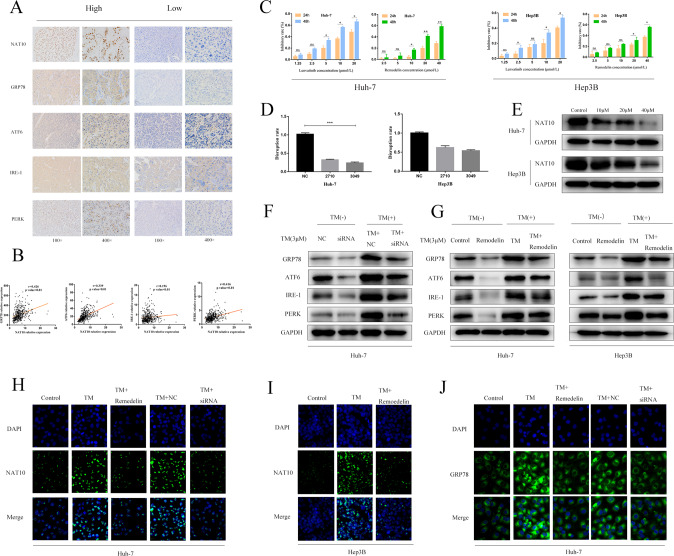
Fig. 2. NAT10 promotes ERS in HCC cells.
A Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to analyze the clinicopathologically collected HCC tissues (n = 100), and the results showed that the expression of four ERS marker proteins was positively correlated with NAT10. B Using the TCGA database, it was found that the correlation analysis between NAT10 and ERS marker proteins in HCC tissues was positive. C CCK-8 method was used to detect the inhibition rate of Lenvatinib and Remodelin on the two cell lines. D qPCR was used to detect the knockdown effect of siRNA on the expression of NAT10 in the two cell lines, and the results showed that Huh-7 alone could knock down the expression of NAT10 by more than 70%. E Western blot showed that Remodelin, a NAT10 inhibitor, significantly inhibited the expression of NAT10 in Huh-7 and hep3B cell lines. F huh-7 cells were treated with NAT10-siRNA for 24 h. Total cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by western blotting using antibodies against GRP78, ATF6, IRE-1, PERK, and GAPDH. G huh-7 and Hep3B cells were treated with Remodelin (20 μmmol/L) for 24 h. Total cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by western blotting with antibodies to GRP78, atf-6, ire-1, PERK, and GAPDH. H The percentage of NAT10(green) in HuH-7 cells increased 24 h after TM (3 μmmol/L) induction, and decreased 24 h after siRNA and Remodelin treatment. I The percentage of NAT10(green) in hep3B cells increased 24 h after TM (3 μmmol/L) induction, and decreased 24 h after siRNA and Remodelin treatment. J After 24 h of TM (3 μmmol/L) induction, the percentage of GRP78(green) in Huh-7 cells increased, and after 24 h of TM induction, the percentage of GRP78(green) in HuH-7 cells decreased after 24 h of siRNA and Remodelin treatment. Each experiment was conducted in triplicate. Data were shown as mean ± standard deviation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.