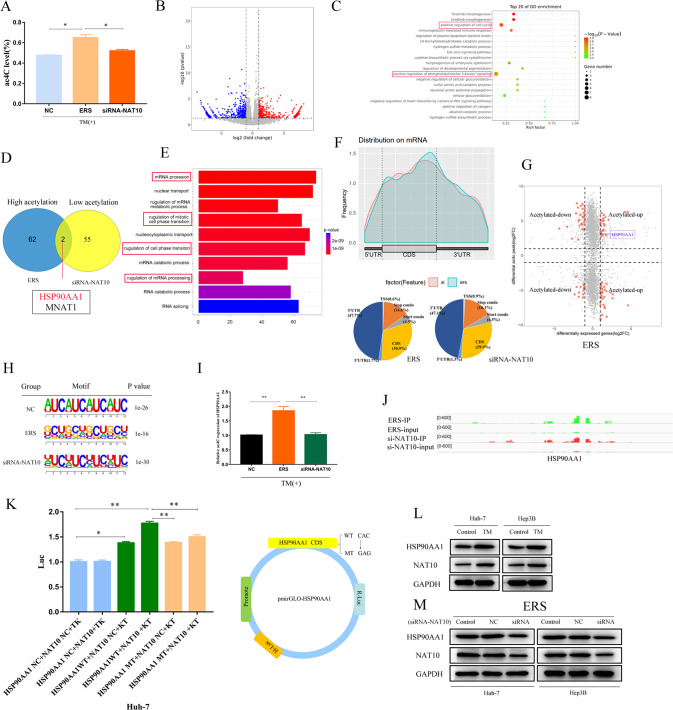
Fig. 5. HSP90AA1 is a downstream regulatory target of NAT10.
Huh-7 cells induced by TM and knocked down by NAT10 were subjected to liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry, ACRIP-Seq, and RNA-Seq. A Compared with the control group, the total amount of mRNA ac4C modification in Huh-7 cells was significantly increased after ERS transfection and significantly decreased after siRNA knockout (P < 0.05). B RNA-seq Volcano plots depicting genes with upregulated (red) and downregulated (blue) mRNA levels. C RNA-seq GO pathway enrichment analysis revealed that the differential genes were located in the cell cycle and extracellular matrix pathways. D Gene overlap was detected by comparing genes upregulated by acetylation in TM-induced HuH-7 cells with genes downregulated by siRNA knockdown. E acRIP-Seq RNA sequence data pathway enrichment analysis showed that NAT10 was associated with mRNA modification and cell cycle. F ac4C peak mainly appeared in the CDS coding region of Huh-7 cells. G The mRNA acetylation level was depicted by the four-quadrant map of ACRIP-Seq analysis. H Typical CXX motif pattern of ac4C peak. I acRIP-qPCR, J HSP90AA1 acetylation peak, K double luciferase reporter assay. L–M HSP90AA1 was positively correlated with NAT10 at the protein level. WB analysis of Huh-7 and Hep3B treated with siRNA-HSP90AA1 compared with control cells transfected with vector. All data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.