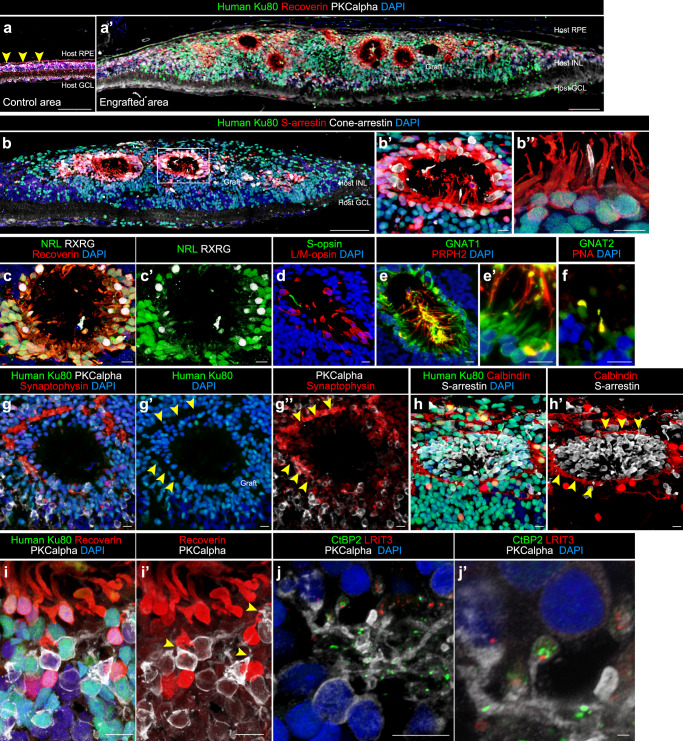
Fig. 6. Engraftment and photoreceptor maturation of iPSC-retinal sheets after subretinal transplantation in RD-nude rats.
a–j’ Immunostaining of rat eyes transplanted with iPSC-S17-derived retinal sheets. The retinal sheets were transplanted in the subretinal space of RD-nude rats. The rat retinas were fixed at 263 days after transplantation (341 days after initiation of differentiation). a, a’ Immunostaining for human Ku80 (green), Recoverin (red), and PKCalpha (white). Control non-transplanted area (a). Engrafted area (a’). Arrowheads in (a): human Ku80−, Recoverin+ and PKCalpha+ rat bipolar cells. b–b” Immunostaining for human Ku80 (green), S-arrestin (red), and Cone-arrestin (white). Boxed area in (b) corresponds to (b’). High magnification in (b’) and higher magnification in (b”). c–h’ Immunostaining for photoreceptor markers. NRL (green), Recoverin (red), and RXRG (white) in (c, c’). S-opsin (green) and L/M-opsin (red) in (d). GNAT1 (green) and PRPH2 (red) in (e, e’). GNAT2 (green) and PNA (red) in (f). Human Ku80 (green), Synaptophysin (red), and PKCalpha (white) in (g–g”). Arrowheads in (g’, g”): Synaptophysin-positive neurites in no nuclear space. Human Ku80 (green), Calbindin (red), and S-arrestin (white) in (h, h’). Arrowheads in (h’): Calbindin-positive neurites. i, i’ Maximum projection image of Z-stacks immunostained for human Ku80 (green), Recoverin (red), and PKCalpha (white) in (i, i’). Note that human Ku80− and PKCalpha+ bipolar cells were located near the human Ku80+ and Recoverin+ photoreceptors (arrowheads). j, j’ Maximum projection image of Z-stacks stained for CtBP2 (green), LRIT3 (red), and PKCalpha (white). High magnification in (j’). Note that photoreceptor-synapse marker CtBP2 and LRIT3 were expressed near the neurites of PKCalpha+ rod bipolar cells. DAPI staining (blue) in (a, a’, b–b”, c, d, e, e’, f, g, g’, h, i, j, j’). Scale bars: 100 µm in (a, a’, b), 10 µm in (b’, b”, c–j), and 1 µm in (j’). INL inner nuclear layer, GCL ganglion cell layer.