Fig. 4. Substitution of HS-binding Hh amino acids affects Drosophila wing patterning.
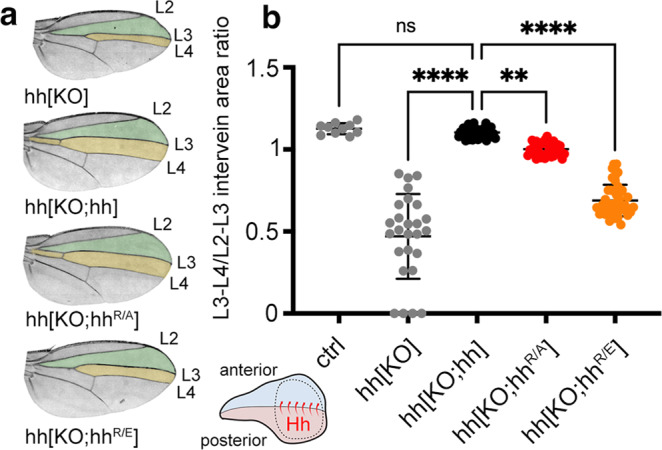
a Hh produced in clones of the posterior wing disc compartment (as shown in the cartoon, Hh is produced in the posterior compartment of the disc and moves over a significant distance35 to the anterior receiving compartment, Supplementary Fig. 5) directly patterns the central domain of the adult wing (orange). Wing patterning beyond the central domain (the green area and the anterior top space that is not colored) depends on Dpp expression. Note that wing-mispatterning phenotypes are similar if due to the lack of Hh production in wing disc clones homozygous for hh[KO] or if homozygous for hh[KO;hhR/E]. Clonal hh expression, in contrast, completely restored wing patterning. b Quantification of wing phenotypes as shown in (a). Wings of female flies developing at 25 °C were analyzed, and Hh function during development was expressed as L3-L4/L2-L3 intervein area ratios. Error bars represent standard deviation. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test, F = 152. n = 10 (hh), n = 26 (hh[KO]), n = 39 (hh[KO;hh]), n = 34 (hh[KO;hhR/A]), and n = 43 (hh[KO;hhR/E]). ****p ≤ 0.0001, **p = 0.0019, ns: p = 0.96. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. No sex bias was observed in any assay. Ctrl: FRT82B donor line.
