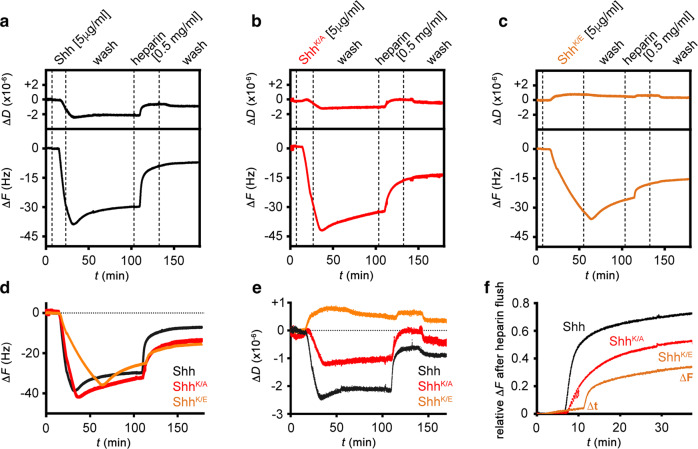
Fig. 6. The second HS-binding site in Shh facilitates cross-linking and switching between heparins.
a–c QCM-D binding assays analogous to Fig. 5, for Shh (a), ShhK/A (b), and ShhK/E (c), with an added step of competition with soluble heparin. d Overlays of frequency responses as shown in (a–c) demonstrate a reduced binding rate and increased unbinding rate in the wash buffer of ShhK/E, and reduced unbinding of ShhK/A and ShhK/E upon competition with soluble heparin, compared to Shh. e Overlay of associated dissipation shifts as shown in (a–c) evidences reduced rigidification of the heparin layer by ShhK/A, and even more so by ShhK/E, compared to Shh, demonstrating that the second HS-binding site is essential for HS cross-linking. f Overlay of frequency responses (relative to full protein elution) from the start of soluble heparin-mediated protein elution (t = 0) until t = 40 min after elution start evidences an overall reduced elution rate for ShhK/A and ShhK/E compared to Shh, thus demonstrating that the second HS-binding site of Shh promotes rapid HS switching.