Figure 6.
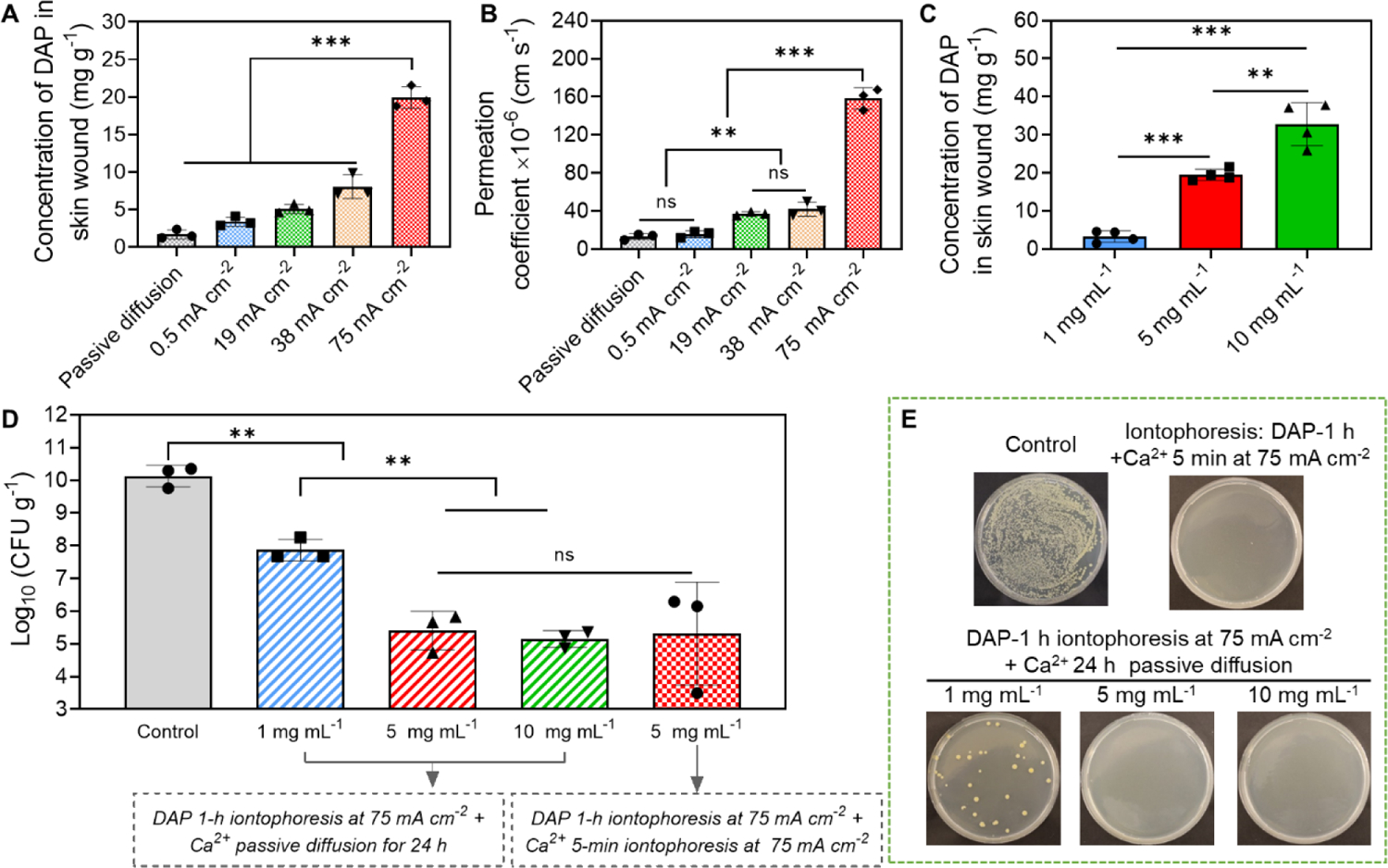
Anti-biofilm efficacy of our electrical biofilm treatment system using DAP. (A-C) Iontophoretic delivery of DAP using our system into an ex vivo MRSA biofilm-infected porcine skin wound model. (A) Accumulated concentration of DAP in wound tissues measured immediately after 1 h iontophoresis at different current intensities. The drug chamber of the working device (cathode) was loaded with 5 mg mL−1 DAP. (B) Permeation coefficient (Pc) of DAP as a function of applied current intensity. (C) Accumulated concentration of DAP in wound tissues measured immediately after 1 h iontophoresis with different DAP loading concentrations. The current intensity was 75 mA cm−2. (D) MRSA bacterial count in wound tissues measured at 24 h after treatment with our system (75 mA cm−2 1-h) using different DAP loading concentrations. Detailed treatment protocols were noted in the figure. (E) Representative photographs of bacterial colony cultured from ex vivo biofilm infected skin wounds after different treatments. All tissue homogenates were diluted 104 times with PBS before plating.
