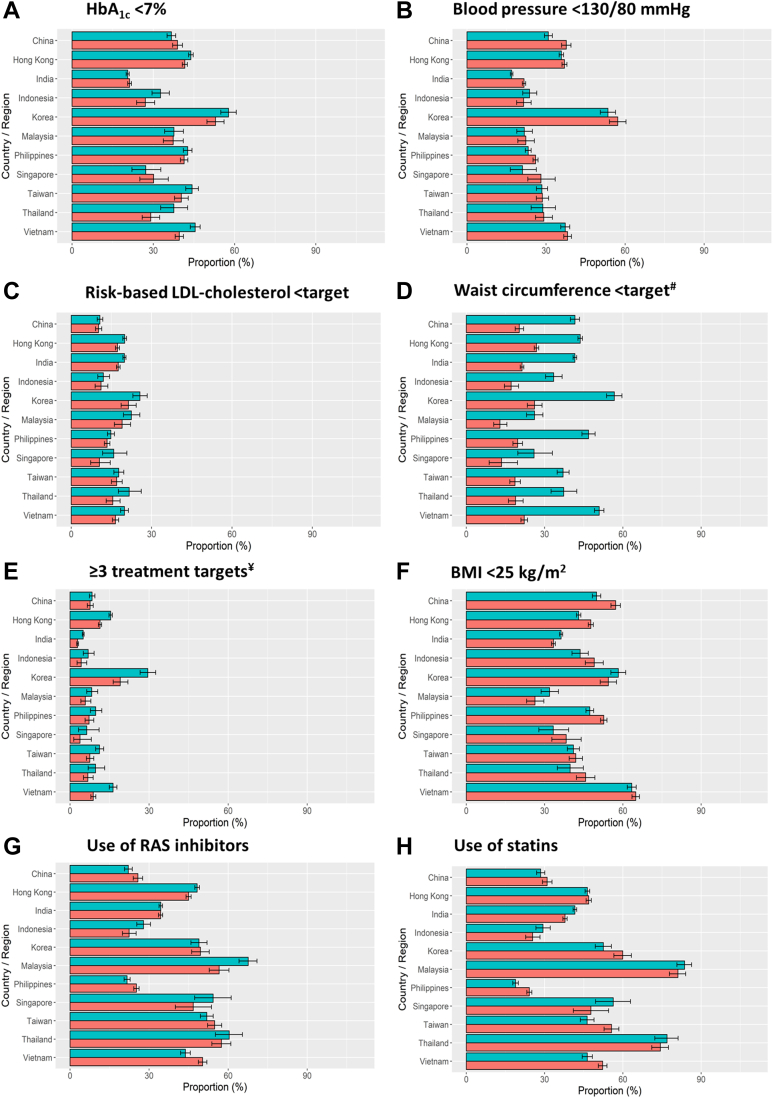
Fig. 2.
Control of cardiometabolic risk factors (HbA1c < 7% (A), blood pressure < 130/80 mmHg (B), risk-based LDL-cholesterol target (C), waist circumference < target (D), ≥3 treatment targets (E) and BMI < 25 kg/m2 (F)) and use of cardiorenal protective drugs (use of RAS inhibitors (G) and use of statins (H)) at registration by countries/areas. Footnotes: Data are available in Supplementary Tables S4–S11. Green bars represent men. Orange bars represent women. γDefinition of CV risk was based on the 2016 European Society of Cardiology/European Atherosclerosis Society (ESC/EAS) recommendations in line with the data collection period. #Treatment targets were defined as HbA1c <7%, blood pressure <130/80 mmHg, risk-based LDL-cholesterol target (<2.6 mmol/L if high risk or <1.8 mmol/L if very high-risk), and lack of central obesity (waist circumference <90 cm in men or <80 cm in women). General obesity was defined as body mass index ≥25 kg/m2. RAS, renin-angiotensin system.