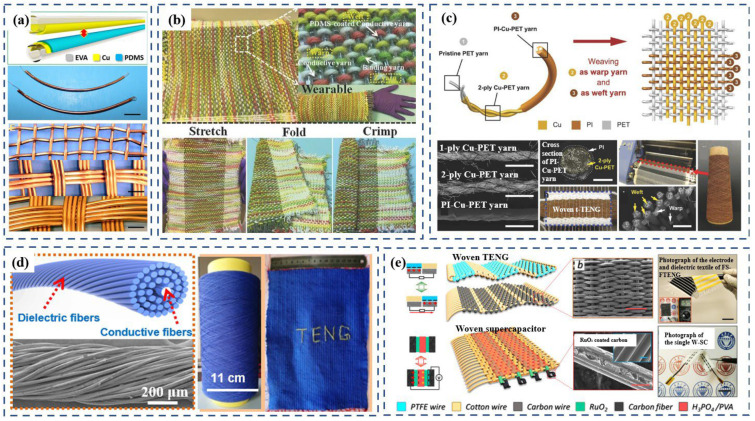
Figure 2.
(a) TENG fabricated from a Cu-coated ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) electrode and a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) covered Cu-coated EVA tubing electrode. Reproduced under the terms of the CC-BY Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0) (accessed on 28 September 2022) [54]. Copyright 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science. (b) Digital photographs of a large-area wearable textile TENG (top view). Bottom views are photographs of the TENG under various mechanical deformations, including stretching, folding, and crimping. Reproduced with permission [55]. Copyright 2017, John Wiley and Sons. (c) TENG fabricated from Cu-coated PET warp yarns and 2-ply PI-coated Cu-PET weft yarns. Reproduced with permission [56]. Copyright 2016, John Wiley and Sons. (d) The core–shell yarn manufactured by 200 elastic spandex fibers tightly twined around two parallel stainless-steel fibers and digital photographs of the TENG. Reproduced with permission [57]. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. (e) Schematic illustration of the free-standing-mode fabric TENG. Reproduced with permission [58]. Copyright 2018, Elsevier.