FIGURE 1.
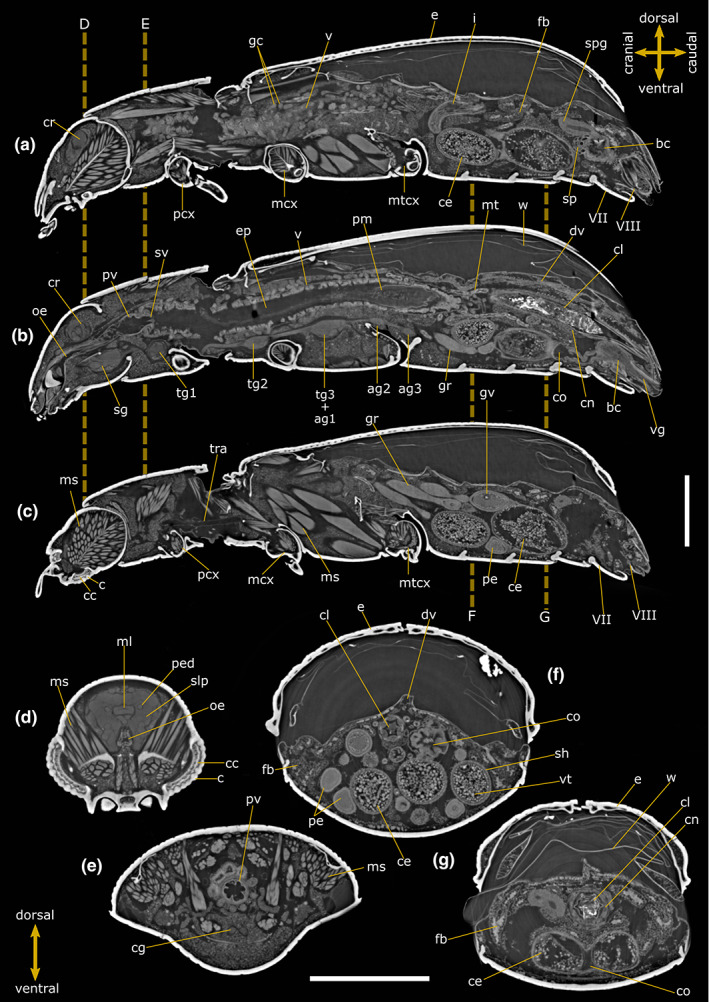
Internal anatomy of Tribolium castaneum female. Two‐dimensional PhC micro‐CT‐based longitudinal (a–c) and cross (d–g) sections. Dashed lines indicate the levels of head (d), pronotum (e) and abdominal (f, g) cross‐sections. VII: Abdominal sternite VII; VIII: Abdominal sternite VIII; ag 2–3: Abdominal ganglia 2 and 3; bc: Bursa copulatrix; c: Cornea; cc: Crystalline cones; ce: Chorionic egg; cg: Connective of ganglia; cl: Colon; cn: Cryptonephridial system; co: Common oviduct; cr: Cerebrum; dv: Dorsal vessel; e: Elytrae; ep: Ectoperitrophic space; fb: Fat bodies; gc: Gastric caeca; gr: Germarium; gv: Germinal vesicle; i: Ileum; mcx: Mesocoxae; ms: Muscle; ml: Median lobe; mt: Malpighian tubules; mtcx: Metacoxae; oe: Oesophagus; pcx: Procoxae; pe: Pre‐vitellogenic egg; ped: Peduncle; pm: Peritrophic matrix; pv: Proventriculus; sg: Suboesophagean ganglion; sh: Epithelial sheath; slp: Superior lateral protocerebrum; spg: Spermathecal gland; sp: Spermatheca; sv: Stomodeal valve; tg1‐2: Thoracic ganglia 1 and 2; tg3 + ag1: Complex of thoracic ganglion 3 and abdominal ganglion 1; tra: Tracheae; v: Ventriculus; vg: Vagina; vt: Vitellum; w: Membranous wings. Scale bars: 500 μm (a–g).
