Table 1.
Classification of natural phenolic compounds.
| Polyphenols | General Structure | Representative Compounds | Antibacterial Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic acids |

|
|
Antibacterial effect increases significantly with pH values [10]. |
| a. Benzoic acid derivatives | |||
| b. Derivates of cinnamic acid |

|
|
|
| Flavonoids |

|
|
Flavonoids act against bacteria such as S. aureus and P. aeruginosa with a very low minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value (0.062 µg/mL) [11]. |
| Lignans |
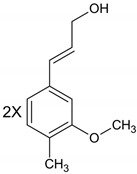
|
|
Due to structural properties, antibacterial activity of lignans is influenced by the stereochemistry of molecules [12]. |
| Stilbenes |
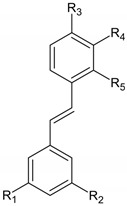
|
|
In combination with antibiotics, some stilbenes can be useful in treating infections caused by multidrug-resistance bacteria [13]. |
| Tannins |
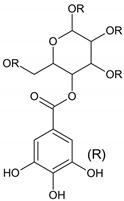
|
|
Tannin compounds act against bacteria, causing disintegration of bacterial colonies, by interfering with the bacterial cell wall and inhibiting fatty acid biosynthesis pathways [14]. |
| a. Hydrolysable tannins | |||
| b. Nonhydrolysable tannins (Condensed tannins) |

|
||
| c. Pseudotannins |

|
