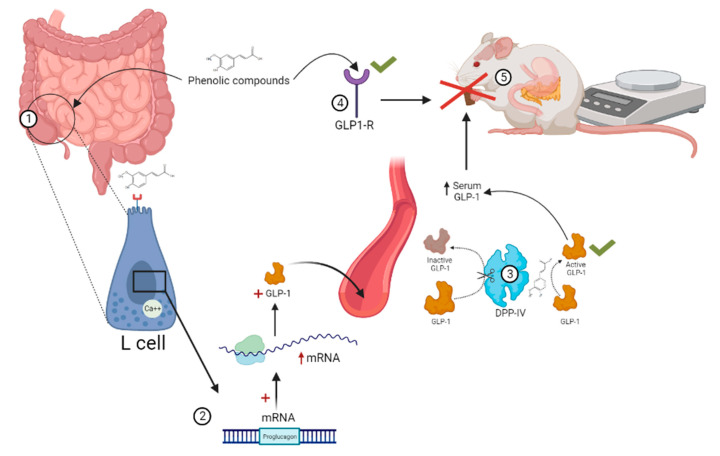
Figure 4.
Potential mechanisms by which phenolic compounds can modulate GLP-1. (1) The ileum and terminal colon contain the highest density of enteroendocrine L-type cells that synthesize and secrete GLP-1. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, ferulic acid, genistein, rutin and hispidulin have shown the ability to increase GLP-1 secretion. (2) Extracts of phenolic compounds increase mRNA expression of the proglucagon gene (GLP-1 precursor). (3) Rutin inhibits the activity of DPP-IV, which inactivates GLP-1, thereby increasing in circulating half-life. (4) Puerarin increases mRNA expression of the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) and signaling. (5) Increased serum GLP-1 after consuming phenolic compounds results in an anorexigenic effect and suppression of body weight gain in vivo.