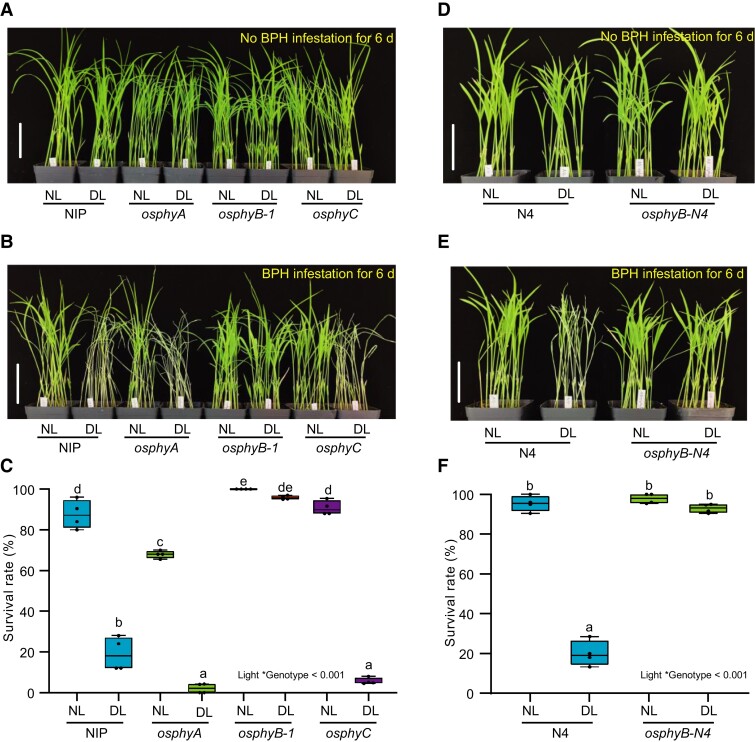
Figure 1.
Dim light reduces BPH resistance through OsPHYB. A, Two-week-old seedlings of wild type Nipponbare (NIP), osphyA, osphyB-1, and osphyC mutants grown under Normal light conditions (NL) and pretreated with NL and dim light (DL) for 24 h, then continuously exposed to NL and DL conditions without BPH infestation for 6 d. Bar, 7 cm. B and C, Representative images (B) and seedling survival rate (C) of NIP, osphyA, osphyB-1, and osphyC at 6 d post infestation (dpi) with BPH under NL and DL treatments. Bar, 7 cm. D, Two-week-old seedlings of wild type Ningjing 4 (N4) and OsPHYB mutant (osphyB-N4) grown under NL conditions and pretreated with NL and DL for 24 h, then continuously exposed to NL and DL conditions without BPH infestation for 6 d. Bar, 7 cm. E and F, Representative images (E) and seedling survival rate (F) of N4 and osphyB-N4 at 6 dpi with BPH under NL and DL treatments. Bar, 7 cm. In C and F, the mean separation tests are shown with box plots. The center lines of the box plots indicate the median, the bounds of the box show the 25th and the 75th percentiles, and the whiskers indicate 1.5 × IQR. n ≥ 3 independent experiments, with each pool including 25 individual plants. Different letters designate significantly different means by 2-way ANOVA + Tukey's post hoc test (P < 0.05). Interaction P value is shown in the inset.