Fig. 2.
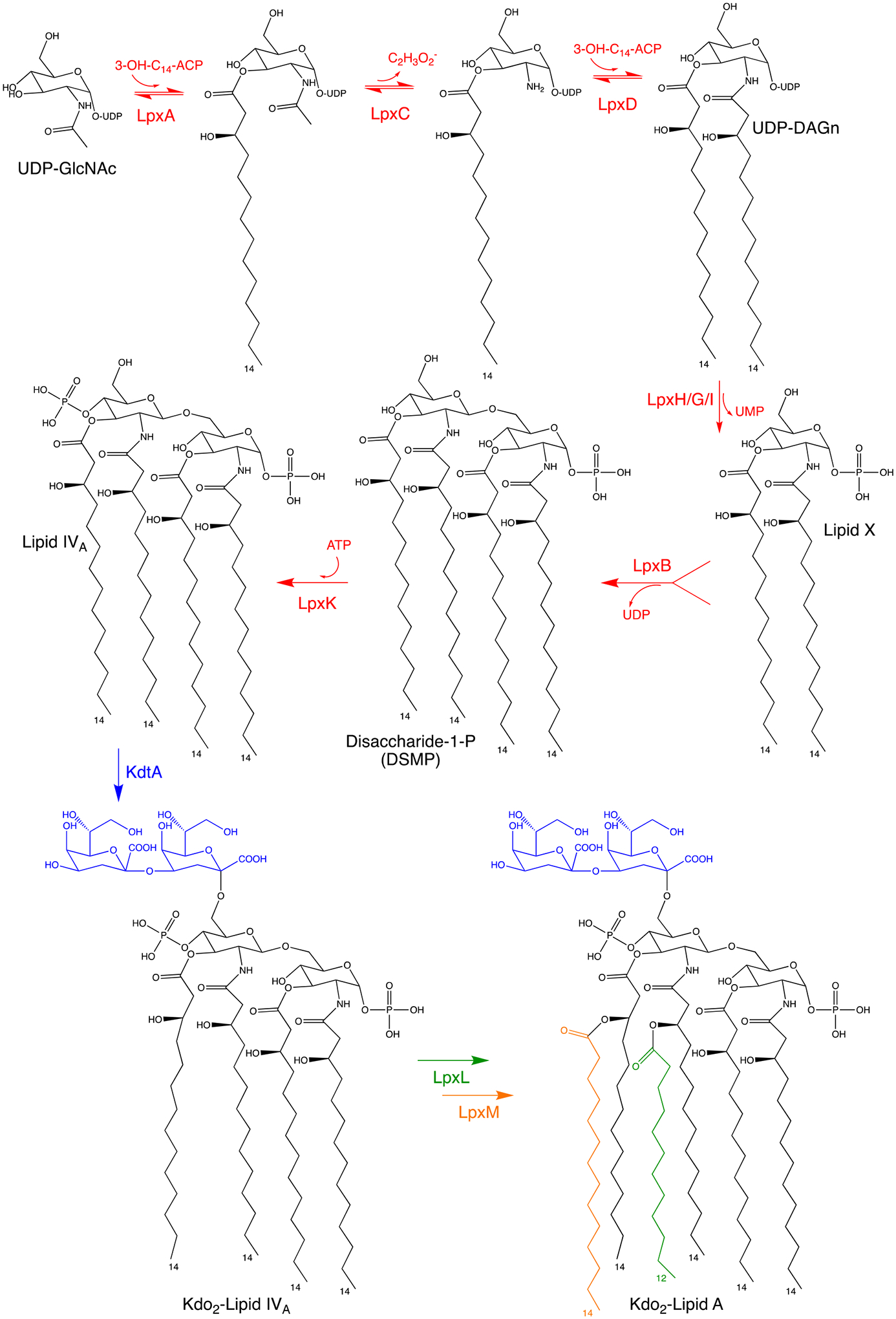
The Raetz pathway of lipid A biosynthesis in E. coli K12. The first six enzymes – LpxA, LpxC, LpxD, LpxH/G/I, LpxB and LpxK – are essential and together catalyze the diacylation of uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc), subsequent condensation of two molecules, and phosphorylation yielding lipid IV A. Three functional orthologs carry out the pyrophosphate cleavage of UDP-DAGn to form Lipid X: LpxH in β-proteobacteria and γ-proteobacteria; LpxI in α-proteobacteria; and LpxG in Chlamydiae. The remaining three enzymes – KdtA, LpxL and LpxM – are non-essential and responsible for the further glycosylation and acylation into Kdo2-lipid A, the final product to which core oligosaccharide and O-antigen are added.
