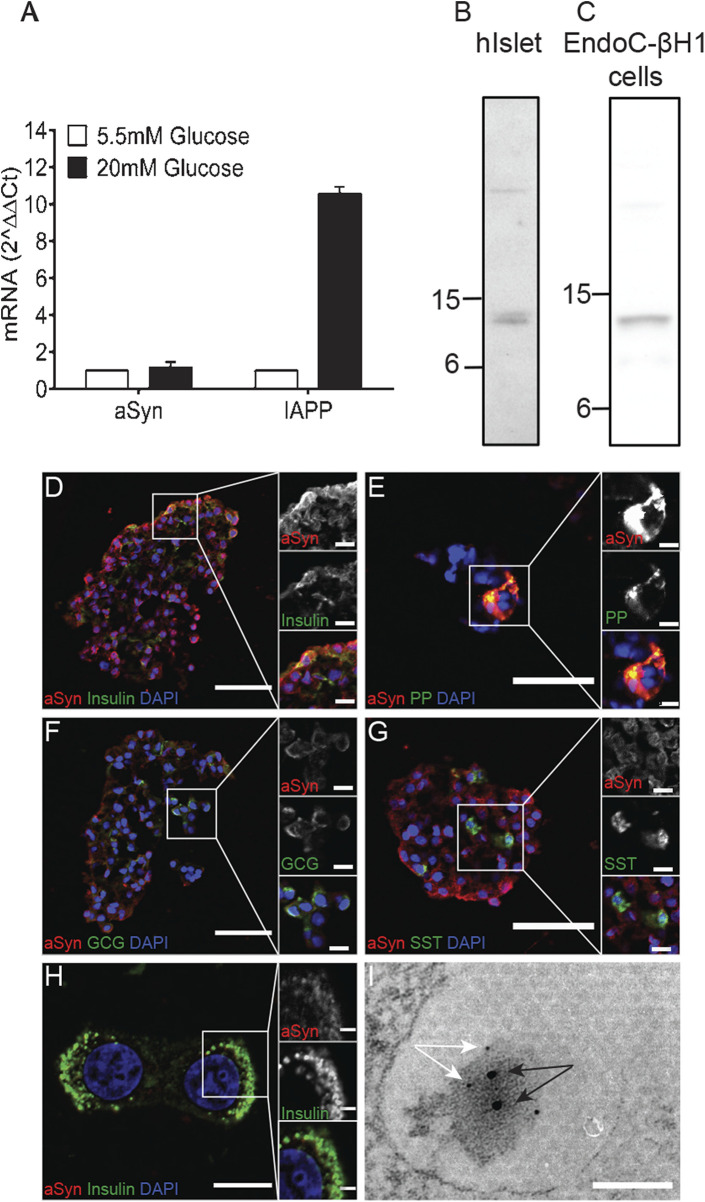
FIGURE 1.
ASyn is present in human islets and human EndoC-βH1 cells. Human islets (n = 2) were divided into two groups and cultured in normal glucose (5.5 mM) or high glucose (20 mM) for 2 days before being analyzed for aSyn mRNA and IAPP mRNA. Data were presented as fold changes, and expression of aSyn mRNA and IAPP mRNA were normalized to GUSb and relative to normal glucose. (A) Culturing in high glucose slightly increased aSyn mRNA levels by 1.18-fold, whereas the same treatment increased IAPP mRNA by 10-fold. Western blot data confirm the presence of aSyn in (B) human islets and (C) human EndoC-βH1 cells as 14 kDa band using aSyn-specific antibody Syn-1. The localization of aSyn in human islets was investigated using double-immunofluorescence staining. ASyn reactivity co-localized with (D) insulin and (E) pancreatic polypeptide, partially co-localized with (F) glucagon, but no co-localization occurred with (G) somatostatin. The co-localization of aSyn and insulin reactivity was also detected in (H) EndoC-βH1 cells. (I) In the electron micrograph, aSyn (10 nm gold particles, black arrows) and insulin (5 nm gold particles, white arrows) reactivity were both detected in secretory granules of β cells, especially around the dense core of granules. Scale bars are 50 μm and 10 µm in insets (D–G), 10 μm and 2 µm in inset (H), and 100 nm in (I).