FIGURE 5.
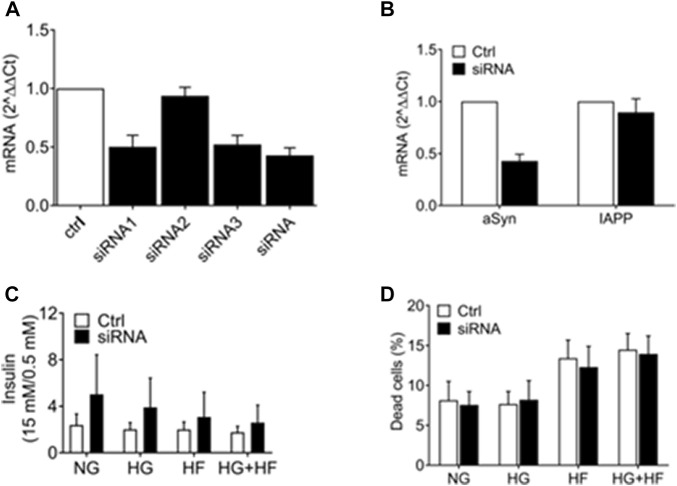
aSyn knockdown did not affect insulin secretion in EndoC-βH1 cells. The efficiency of 3 different aSyn siRNAs was tested in EndoC-βH1 cells, and mRNA levels were analyzed at 48 h post-transfection. (A) SiRNA1, siRNA3, and pooled siRNA (siRNA) reduced aSyn mRNA level by 50%. SiRNA2 did not reduce aSyn mRNA level. (B) SiRNA reduced aSyn mRNA level while did not alter IAPP mRNA level. Data were normalized to GUSb and correlated to control siRNA. Transfected EndoC-βH1 were exposed to normal glucose (5.5 mM, NG), high glucose (20 mM, HG), high fat (1.5 mM sodium palmitate, HF) or high glucose plus high fat (20 mM glucose and 1.5 mM sodium palmitate, HG + HF) condition for 48 h before being analyzed. (C) Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) was analyzed using alphaLISA, where no significant difference in GSIS fold change was observed between the control and siRNA-treated group in all 4 culture conditions (NG, HG, HF, HG + HF). (D) The viability of cells was analyzed by propidium iodide (PI) staining using flow cytometry, where no significant difference in dead cell proportion was observed between the control and siRNA-treated group in all 4 (NG, HG, HF, HG + HF) culture conditions. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test, mean ± SD, n = 3.