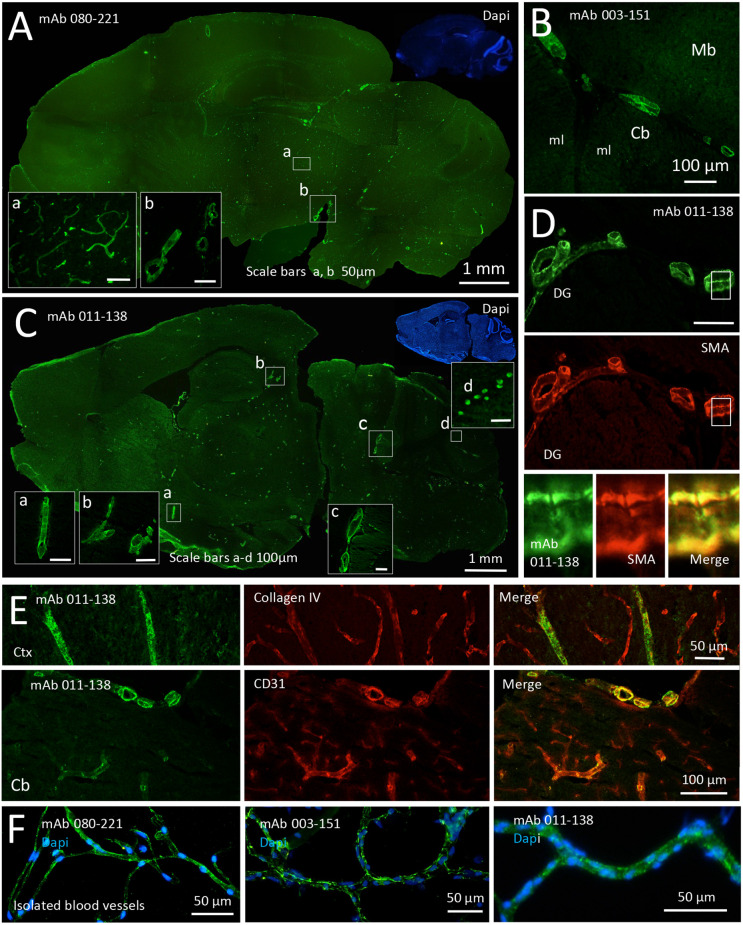
Figure 2.
Recombinant monoclonal antibodies from NMDAR encephalitis patients bind to brain blood vessels and Purkinje cells. Unfixed and unpermeabilized sections from adult mouse brains were incubated with 5 μg/ml of the respective human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) obtained from three different patients diagnosed with NMDAR encephalitis. Visualization of tissue binding was performed using a FITC-coupled anti-human IgG secondary antibody. (A) Sagittal brain section incubated with mAb 080-221. Prominent staining of large to small blood vessels including capillaries was obtained in all brain regions (see insets a and b). (B) Sagittal brain section incubated with mAb 003-151. Prominent staining of large to mid-size blood vessels in all brain regions was obtained (a section of cerebellum, Cb, and midbrain, Mb, is shown; ml molecular layer). (C) Sagittal brain section incubated with mAb 011-138. Prominent staining of large to mid-size blood vessels in all brain regions was obtained (see insets a, b, and c). In addition to blood vessel staining cerebellar Purkinje cells showed marked somatic staining (see inset d). (D) Double staining against human IgG and SMA (smooth muscle actin) in a brain section adjacent to the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus formation. Bound human IgG was mainly detected within the SMA-positive muscle layer of the vessels. (E) Double stainings against Collagen IV (upper panel) and CD31 (lower panel) confirm immunoreactivity of mAb 011-138 to blood vessels. Ctx Cortex (F) Staining of isolated brain blood vessels. Blood vessels were obtained from homogenized mouse brains by combinatory centrifugation and filtering steps. A 30–100 μm filter size fraction incubation with all three antibodies resulted in clear staining of the vessels within this fraction. Note that the diameter of mounted blood vessels is subject to shrinking artifacts during the staining procedure.