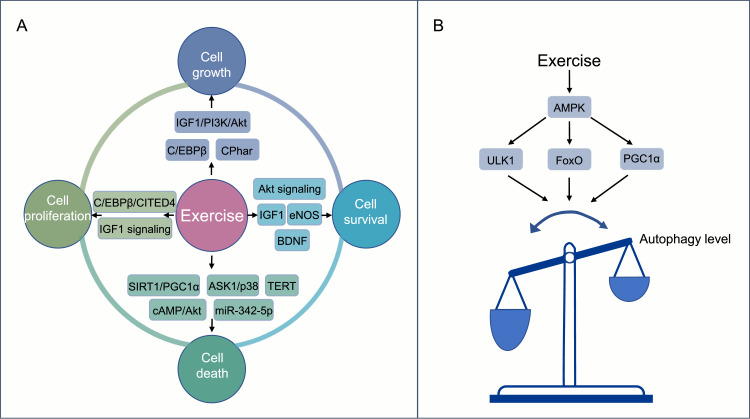
Fig. 4.
Benefits of exercise for recycling and turnover. (A) The critical regulators and signaling pathways involved in the positive effects of exercise on cellular remodeling, including cell proliferation, cell growth, cell survival, and cell death; (B) The regulation of autophagy during exercise training. The common regulatory pathways underlying exercise-induced autophagy involve the activation of the AMPK-ULK1 signaling pathway, FoxO, PGC1α, etc. AMPK = adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase; ASK1 = apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; BDNF = brain-derived neurotrophic factor; cAMP = cyclic adenosine monophosphate; C/EBPβ = CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β; CITED4 = CBP/p300-interacting transactivators with E (glutamic acid)/D (aspartic acid)-rich-carboxyl terminal domain; CPhar = cardiac physiological hypertrophy-associated regulator; eNOS = endothelial nitric oxide synthase; FoxO = forkhead box O; IGF1 = insulin-like growth factor 1; miR = microRNA; PGC1α = peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor coactivator 1α; PI3K = phosphoinositide 3-kinase; SIRT1 = sirtuin 1; TERT =telomerase reverse transcriptase; ULK1 = unc-51-like kinase 1.