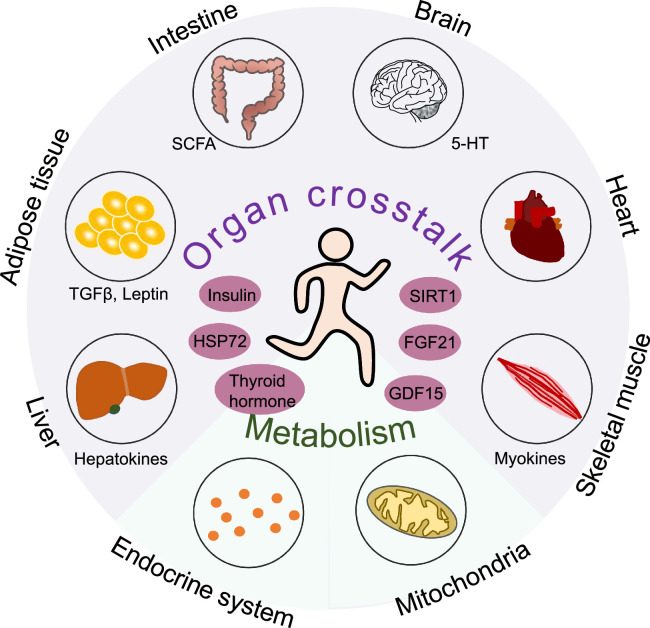
Fig. 5.
Exercise has systemic effects. Exercise leads to systemic effects by evoking the coordinated and integrated adaptation of multiple organ systems. Exercise results in the secretion of myokines, adipokines (e.g., TGFβ, leptin), and hepatokines as well as by-products of gut microbiota (e.g., SCFA) that have key roles in interorgan communication and, thus, mediate many of the beneficial effects of exercise. 5-HT = serotonin; FGF21 = fibroblast growth factor-21; GDF15 = growth differentiation factor-15; HSP72 = heat shock protein 72; SCFA = short-chain fatty acids; SIRT1 = sirtuin 1; TGFβ = transforming growth factor-β.