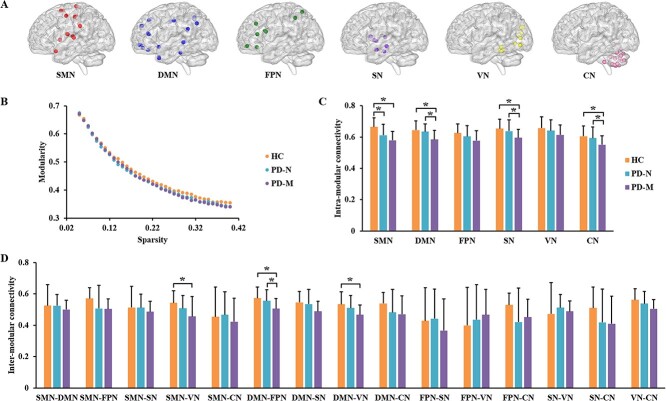
Figure 3.
Modular characteristics of functional brain networks in the three groups. (A) Six modules which were identified using combined data from all three groups: Details are given in supplementary materials. (B) Network modularity (Q) as a function of sparsity: Modularity Q monotonically decreased as a function of increasing cost, the AUC of which did not differ among the three groups. The bar graphs show data with post hoc pairwise comparisons showing significant between-group differences in (C) intramodular and (D) intermodular connectivity. Abbreviations: PD, Parkinson’s disease; PD-M, PD with mild cognitive impairment; PD-N, PD with normal cognition; HC, healthy controls; SMN, sensorimotor network; DMN, default mode network; FPN, frontal–parietal network; SN, subcortical network; VN, visual network; CN, cerebellum network.