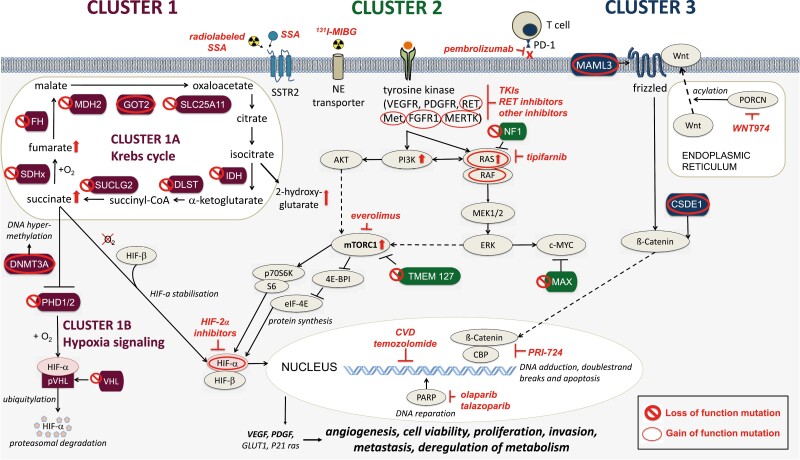
Figure 1.
The 3 main molecular clusters of PPGLs and their associated gain (○) or loss (○) of function mutations. Cluster 1 mutations (crimson) include mutations in cluster 1A/Krebs cycle-related genes (SDHx, FH, MDH2, GOT2, SLC25A11, IDH, DLST, SUCLG2) and cluster 1B/hypoxia signaling-related genes (PHD1/2, VHL, HIF2A/EPAS1). These mutations lead to an accumulation of oncometabolites, increased DNS hypermethylation, decreased HIF-α degradation and HIF-α stabilization. Cluster 2 mutations (green) disrupt the kinase signaling pathway and lead to their overactivation (RET, MET, FGFR1, MERTK, NGFR, NF1, HRAS, BRAF, TMEM127, MAX). Cluster 3 mutations (blue) affect the Wnt signaling pathway (MAML3, CSDE1). All mutations may lead to increased angiogenesis, cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and deregulation of metabolism. Potential therapies are shown in red. ⇧ protein activation or upregulation; ⊥ protein inhibition.