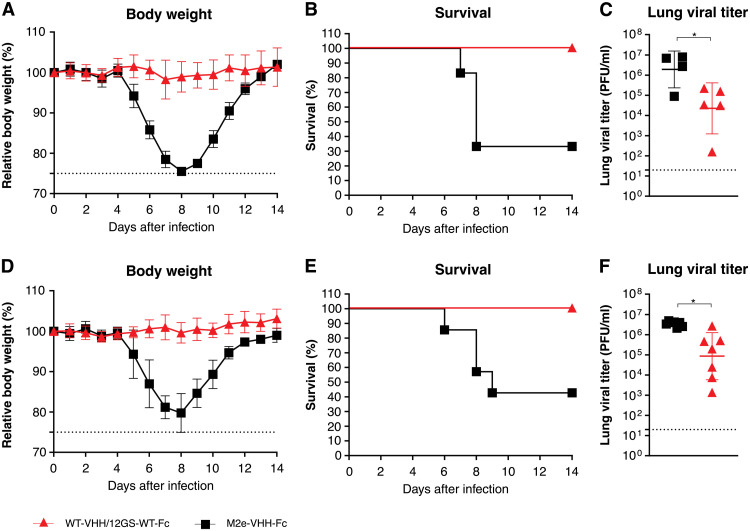
Fig. 1. WT-VHH/12GS-WT-Fc protects K18-hACE2 transgenic mice against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
(A to C) Mice received WT-VHH/12GS-WT-Fc (5 mg/kg; n = 17) or control M2e-VHH-Fc by intraperitoneal injection (n = 10). Mice were challenged 7 hours later with 8 × 103 PFU of SARS-CoV-2. (A) Body weight was measured over the course of infection and plotted relative to starting body weight. Symbols represent means ± SD; P < 0.0001 by a two-way ANOVA. (B) Survival after challenge with SARS-CoV-2 is shown; P = 0.0015 by Mantel-Cox test. (C) Lung viral loads were determined on day 3 after infection from euthanized mice. *P < 0.05 by an unpaired t test. Data in (A) and (B) are pooled from two independent experiments. (D to F) Mice received 20 μg of either WT-VHH/12GS-WT-Fc (n = 15) or M2e-VHH-Fc (n = 14) intranasally. Mice were challenged 7 hours later with 8 × 103 PFU of SARS-CoV-2, and body weight loss [(D) symbols represent means ± SD, P < 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA] and survival [(E) P = 0.0148 by Mantel-Cox test] are shown. (F) Lung viral loads were determined on day 3 after infection from euthanized mice (n = 7 per group). *P < 0.05 by an unpaired t test with Welsh correction. Symbols in (C) and (F) represent individual mice and lines indicate means ± SD. Dotted lines in (C) and (F) indicate lower limit of detection.