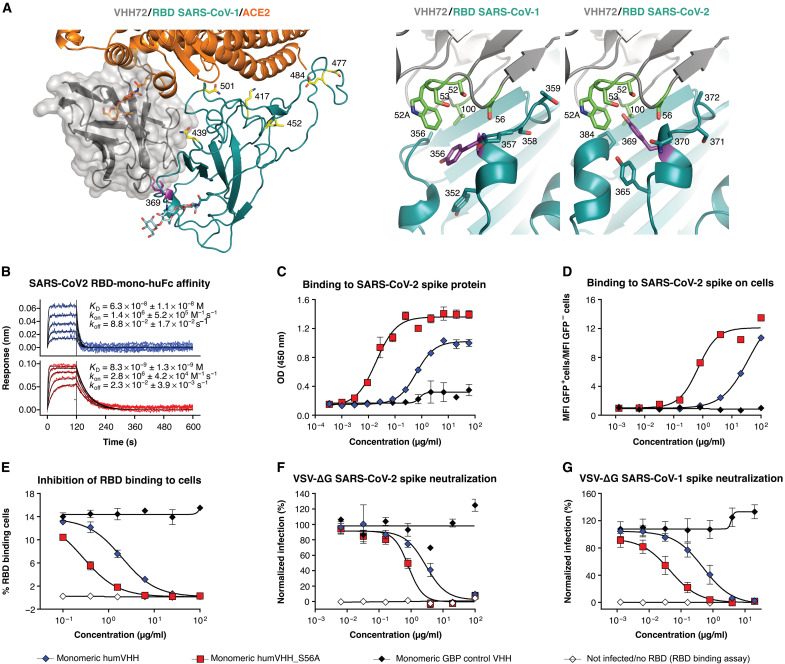
Fig. 2. A computationally predicted VHH72 variant demonstrates enhanced neutralizing activity.
(A) Left: Composite structure overlay of VHH72 (gray), ACE2 (orange), and SARS-CoV-2 RBD (cyan). RBD Tyr369, Lys417, Asn439, Leu452, Ser477, Glu484, and Asn501 are shown as sticks. ACE2 Asn322 and RBD Asn343 N-glycans are shown as orange and cyan sticks, respectively. Right: Close-up view of VHH72 bound to SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 RBD (cyan) based on PDB entry 6WAQ and, for SARS-CoV-2 RBD, a homology model. Residues in CDR2 and CDR3 of VHH72 and of the RBDs that are in close proximity are shown as sticks. SARS-CoV-1 RBD Tyr356 is oriented downward, and its counterpart Tyr369 in the SARS-CoV-2 RBD is oriented upward. (B) BLI sensorgrams of humVHH (top) and humVHH_S56A (bottom) are shown as a twofold dilution series starting at 100 nM to measure binding to immobilized SARS-CoV-2 RBD fused to a monomeric human IgG Fc. Blue and red lines represent double reference–subtracted data and the fit of the data to a 1:1 binding curve is in black. KD is dissociation constant, kon is on-rate, and koff is off-rate. (C) humVHH and humVHH_S56A binding to SARS-CoV-2 spike as measured by an ELISA is shown. Data points indicate means ± SEM; N = 3. (D) humVHH and humVHH_S56A binding to HEK293 cell surface expressed SARS-CoV-2 spike was determined by flow cytometry. GFP fluorescence is shown normalized to the mean GFP fluorescence of noninfected and infected PBS-treated cells. GBP, GFP-binding protein (a VHH directed against GFP); MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. (E) Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 RBD binding to Vero E6 cells was determined by flow cytometry (means ± SD, N = 3). (F) Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 spike VSV pseudotypes and (G) SARS-CoV-1 spike VSV pseudotypes by humVHH and humVHH_S56A was measured by fluorimetry. Symbols represent means ± SD (N = 4).