FIGURE 1.
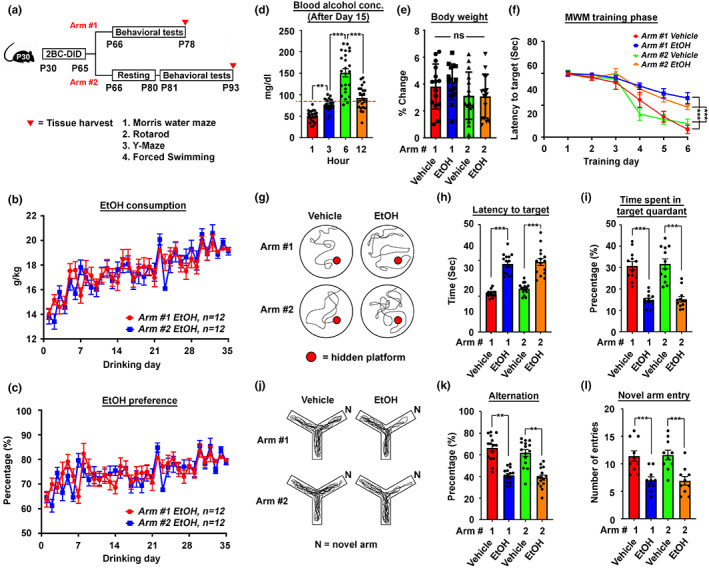
Mouse 2BC‐DID paradigm revealed lasting cognitive and memory impairments. (a) The schematic diagram illustrates the timeline of the 2BC‐DID treatment paradigm with P30 C57BL/6 mice. Arms #1 and #2 represent two treatment arms with behavioural tests being immediately carried out right after the entire drinking program or being delated after a 14‐day resting period. (b) Ethanol consumption trends and (c) preference of mice in Arms #1 and 2 along the entire 2BC‐DID treatment paradigm (N = 12). (d) Blood alcohol concentration of all alcohol‐administering mice in both Arms #1 and #2 at different time points after the initiation of drinking at day 15 (N = 24, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001, one‐way ANOVA). (e) Percentage body weight changes in mice from all arms and all treatments measured on the day after Day 35 of the drinking paradigm relative to the day before drinking treatment started (N = 12, ns = non‐significant, one‐way ANOVA). (f) The latency to target plot during the training phase (Day 1 to Day 6) in the Morris water maze (MWM) test (N = 12, ***p < 0.0001, two‐way ANOVA). (g) Representative swimming patterns of mice in different treatment arms during the MWM probe trial performed on Day 7. (h) The latency to target and (i) the time spent in target quadrant plots of the probe trial in the MWM test (N = 12, ***p < 0.0001, one‐way ANOVA). (j) Representative walking patterns of mice in different treatment arms in a Y‐maze paradigm. (k) The percentage of alternation and (l) the number of novel time entry was recorded and calculated (N = 12, **p < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001, one‐way ANOVA). Values represent the mean ± SEM.
