FIGURE 5.
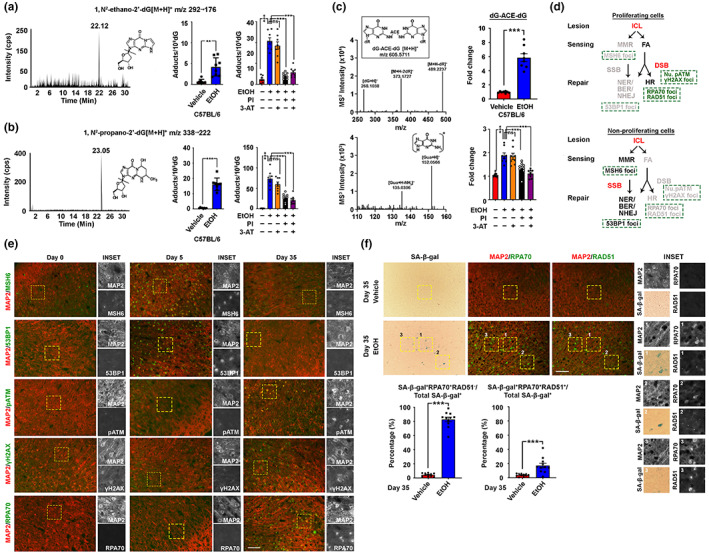
Prolonged ethanol exposure results in DNA‐repair infidelity in cortical neurons. (a) Quantifications of 1, N2‐ethanol‐2′‐dG and (b) 1, N2‐propano‐2′‐dG adducts in brain cortical tissues (N = 8, ***p < 0.0001, two‐tailed unpaired t‐test) and primary cortical neuron subjected to the CIE and drug co‐treatment for 72 h (10 μM PI and 20 μM 3‐AT) (N = 8, ***p < 0.0001, **p < 0.001, *p < 0.01, one‐way ANOVA). (c) Product ion spectra of acetaldehyde‐induced DNA crosslinks measured as dinucleosides. Quantification of their relative abundances in brain cortical tissues (N = 8, ***p < 0.0001, two‐tailed unpaired t‐test) and primary cortical neuron subjected to the CIE and drug co‐treatment for 72 h (10 μM PI and 20 μM 3‐AT) (N = 8, ***p < 0.0001, **p < 0.001, *p < 0.01, one‐way ANOVA). (d) Schematic diagram showing the possible repair pathways for ICL lesions in proliferating and non‐proliferating cells. (e) Representative immunofluorescent staining images of the prefrontal cortex regions of brain samples harvested from mice subjected to different length periods of the 2BC‐DID paradigm (N = 10, scale bar: 200 μm). (f) Representative SA‐β‐gal and immunofluorescent staining images indicating the relationship between cellular senescence and the failure of RPA1 (i.e., RPA70) and RAD51 exchange in neurons. Quantifications were shown (N = 10, ***p < 0.0001, two‐tailed unpaired t‐test, scale bar: 200 μm). Values represent the mean ± SEM.
