Figure 1.
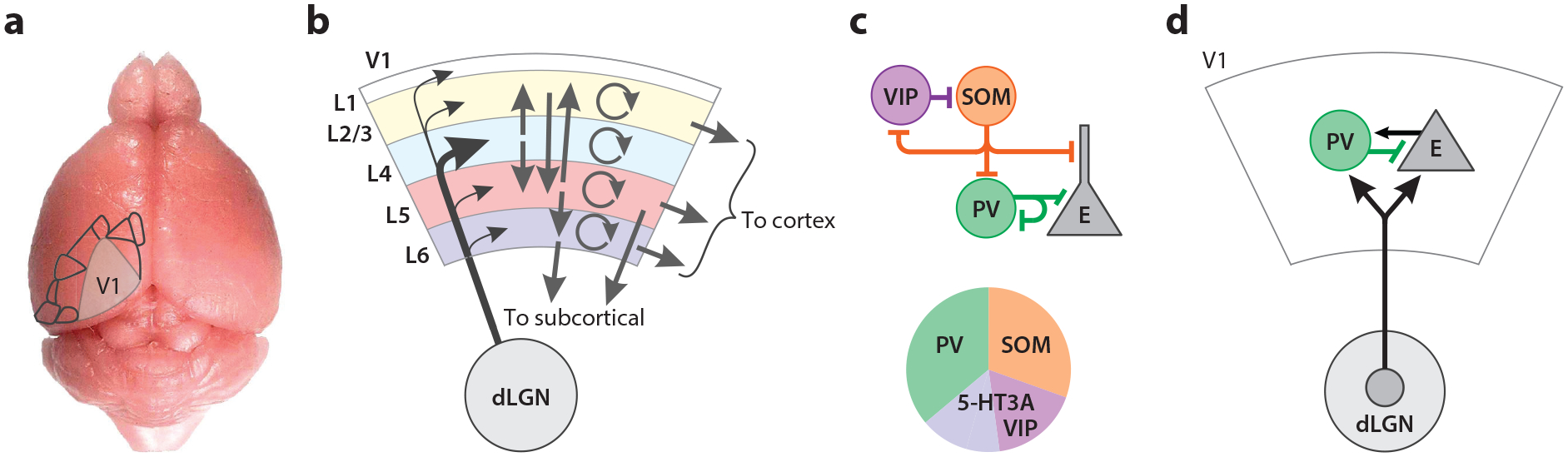
Canonical circuits of mouse visual cortex. (a) Overlay of V1 and higher visual areas on the mouse brain showing location and relative size. (b) Summary of layer-specific excitatory connectivity. V1 outputs project to higher visual areas and other cortical regions as well as many subcortical targets, including structures involved in behavioral output such as superior colliculus and basal ganglia. Panel b adapted from Ji et al. (2016), Jiang et al. (2015), Morgenstern et al. (2016), and Seeman et al. (2018). (c) Summary of inhibitory connectivity motifs. Panel c adapted from Karnani et al. (2016), Lee et al. (2010), and Pfeffer et al. (2013). (d) Thalamocortical input targets both excitatory neurons and PV-positive inhibitory neurons. Panel d adapted from Ji et al. (2016), Jiang et al. (2015), and Seeman et al. (2018). See the Supplemental Appendix for further overview of anatomical circuit organization. Abbreviations: dLGN, dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus; E, excitatory; L, layer; PV, parvalbumin; SOM, somatostatin; V1, primary visual cortex; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide.
