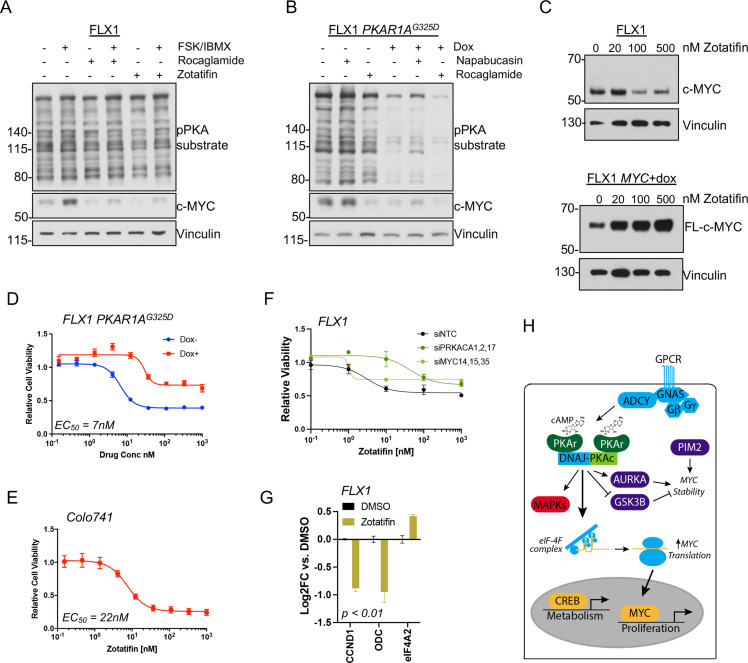
Figure 7. PKA effects on c-MYC are blocked by eIF4A inhibition.
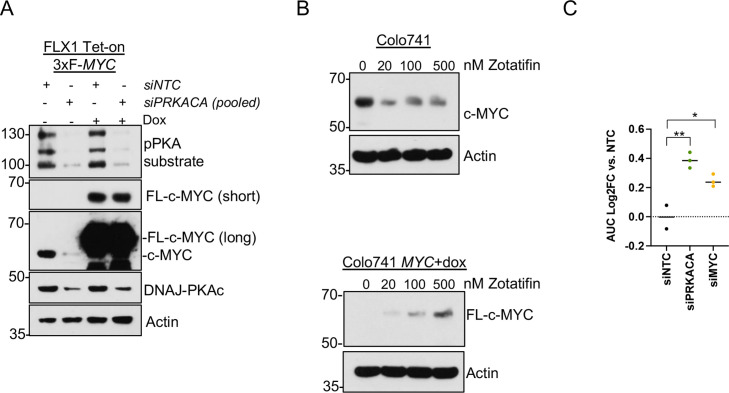
(A) Immunoblots showing the c-MYC protein levels in FLX1 cells after treatment with 100 nM rocaglamide or zotatifin for 24 hr and/or 50 μM forskolin (FSK)/3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX) for 4 hr. (B) Immunoblots showing the change of c-MYC level in engineered FLX1 cells with doxycycline (dox)-inducible 3xFLAG-PRKAR1AG325D after dox induction for 48 hr and treatment with 1 μM napabucasin or 100 nM rocaglamide for 24 hr. (C) Parental FLX1 cells or FLX1 with 48 hr dox-induced 3xFLAG-MYC lacking a 5’UTR treated with escalating doses of zotatifin for 24 hr and blotted for c-MYC. (D) Impact of 72 hr of a dose curve of zotatifin alone or in combination with dox-induced 3xFLAG- PRKAR1AG325D on FLX1 viability by Cell Titer-Glo. Results from technical replicates of a representative experiment ± SD relative to DMSO for each curve. (E) Parental Colo741 treated as in D. (F) Zotatifin sensitivity tested in FLX1 as in D, following siRNA knockdown of PRKACA or MYC. Results combined from three siRNA. Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) confirmation of knockdown is shown in Figure 1C. (G) Impact of 24 hr 100 nM zotatifin on c-MYC targets by qRT-PCR; eIF-4A2 induction is a known effect of zotatifin and is shown as a control. Mean of technical replicates from one representative experiment is shown ± SD, p value determined with two-tailed Student’s t-test. (H) Schematic of DNAJ-PKAc mediating cell proliferation in fibrolamellar carcinoma (FLC) by increasing c-MYC expression by increased translation, with additional effects via GSK3B, AURKA, and PIM2.