FIGURE 2.
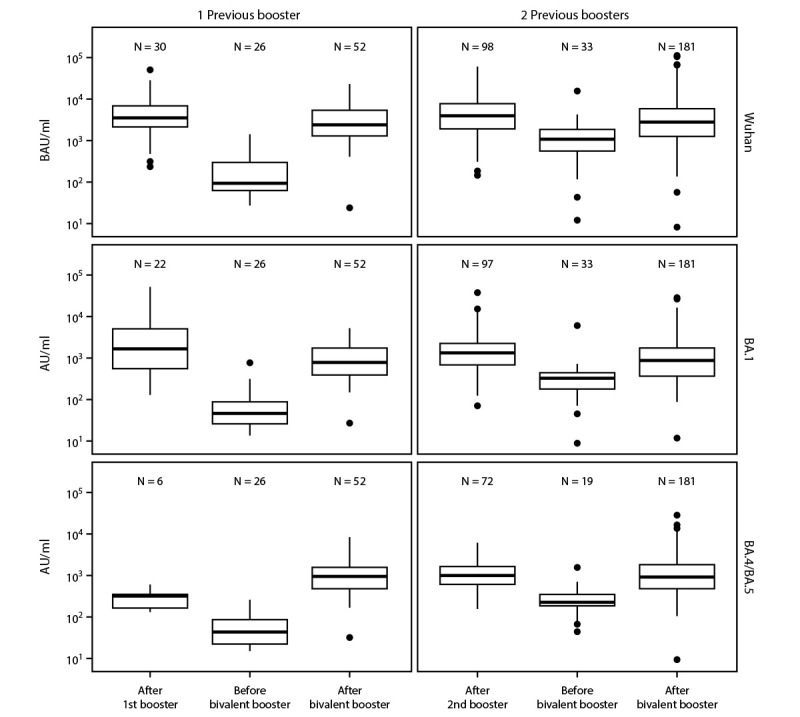
Anti-spike antibody assay results for Wuhan (top panels), Omicron BA.1 (middle panels), and Omicron BA.4/BA.5 strains (bottom panels)* in nursing home residents after receipt of 1 (left panels) or 2 (right panels) previous monovalent booster doses and before and after receiving a COVID-19 bivalent booster dose† — Ohio and Rhode Island, September–November 2022
Abbreviations: AU = arbitrary units; BAU = binding antibody units.
* Anti-spike levels for BA.1 and BA.4/BA.5 are in arbitrary units (AU/mL) with an internal standard allowing comparison across timepoints in this dataset. Wuhan-anti-spike is in binding antibody units (BAU/mL) that are based on the World Health Organization 20/136 standard. The center line indicates the median, and the bottom and top of the box indicate the first and third quartile, respectively. The lower and upper whiskers extend from the first and third quartile lines, respectively, to the smallest and largest values no more than 1.5 times the IQR (height of box) away from the first and third quartile values. Values beyond that appear as points.
† Testing after receipt of booster doses occurred a median of 17 days after vaccination in all groups. In the group that received 1 monovalent booster dose, testing before bivalent dose occurred 11 months after receipt of the first booster dose and a median of 48 days before receipt of the bivalent booster dose. In the group that received 2 monovalent booster doses, testing before the bivalent dose occurred 3 months after receipt of the second booster dose and a median of 49 days before administration of the bivalent booster dose.
