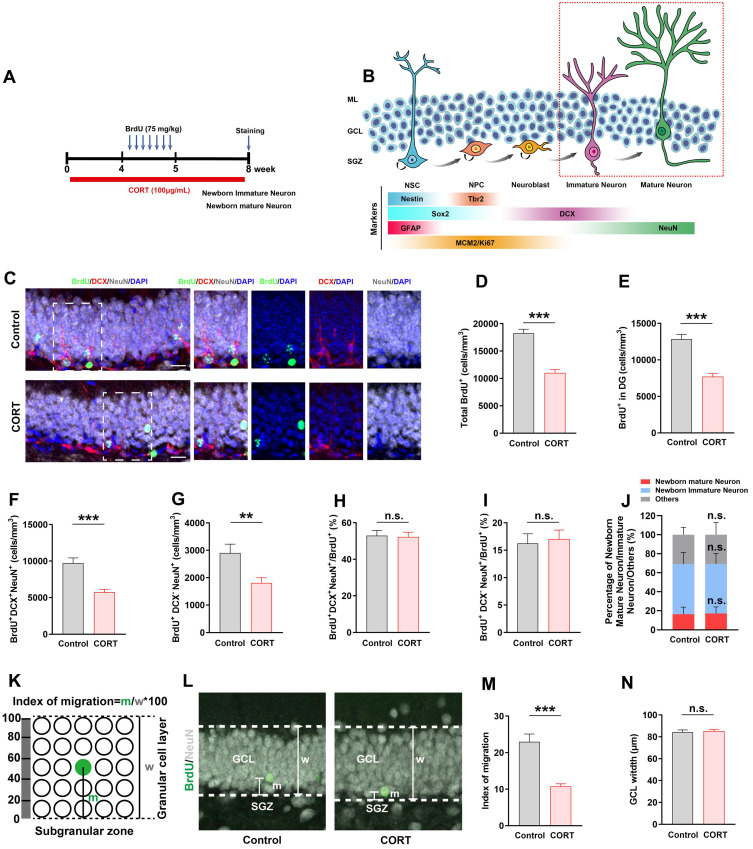
Figure 4.
Chronic CORT treatment impairs the survival of newborn immature/mature neurons and suppresses the migration of newborn mature neurons. (A) Timeline of the experimental procedure. (B) Diagram of the AHN lineage and the markers used to identify the different cell types. (C) Representative images of the control and CORT DG with triple immunostaining of BrdU+ (green), DCX+ (red), and NeuN+ (gray) cells. (D) Quantification of total BrdU+ cells in the DG, hilus and molecular layer. n = 4 mice per group, P < 0.0001. (E) Quantification of BrdU+ cells in the DG. n = 4 mice per group, P < 0.0001. (F) Quantification of BrdU+DCX+NeuN+ cells. n = 4 mice per group, P < 0.0001. (G) Quantification of BrdU+DCX-NeuN+ cells. n = 4 mice per group, P < 0.0001. (H) Quantification of BrdU+DCX+NeuN+ cells/total BrdU+ cells. n = 4 mice per group, P = 0.8490. (I) Quantification of BrdU+DCX-NeuN+ cells/total BrdU+ cells. n = 4 mice per group, P = 0.7392. (J) Proportion of newborn mature neurons, newborn immature neurons, and other newborn cells among all newborn cells. n = 4 mice per group, P > 0.05. (K) Schematic representation of the calculation method used for assessing the migration of newborn neurons in GCL. (L) Representative images showing the migration of newborn mature neurons (BrdU+NeuN+) in GCL. (M) Quantification of the migration index in CORT and control mice. n = 4 mice per group, P < 0.0001. (N) Quantification of the GCL width. n = 4 mice per group, P = 0.7087. Scale bar = 20 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Two-tailed unpaired t-test was used to identify statistically significant differences between datasets (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 when compared to the control group). n.s., non-significant difference.