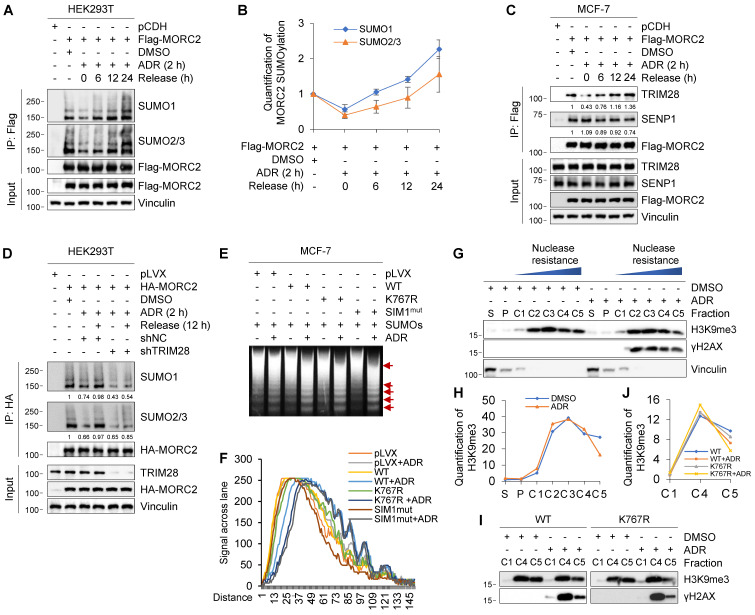
Figure 5.
Transient MORC2 deSUMOylation in response to genotoxic stress. (A-B) HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-MORC2 for 48 h and then treated with or without 1 μM ADR for 2 h, followed by release for the indicated times. Cellular lysates were subjected to IP assays using anti-Flag beads, followed by immunoblotting to detect the SUMOylation levels of MORC2 (A). Quantitative results of SUMO modification levels of MORC2 are shown in B. (C) MCF-7 cells stably expressing pCDH and Flag-MORC2 were treated with or without 1 μM ADR for 2 h, followed by release for the indicated times. Cellular lysates were subjected to IP assays with anti-Flag beads, followed by immunoblotting analysis. (D) HEK293T cells transfected with HA-MORC2 alone or in combination with shNC or shTRIM28 were treated with 1 μM ADR for 2 h, followed by release for 12 h. Lysates were subjected to IP assays with anti-HA beads, followed by immunoblotting analysis. (E) MCF-7 cells stably expressing control vector, WT, K767R or SIM1mut MORC2 were treated with or without 1 μM ADR for 2 h, followed by MNase assays. The arrows indicate the positions of nucleosomal DNA ladders, including mono-, di-, tri- and multiple-nucleosomal DNA. (F) The quantification of signal in each lane of the gel was conducted using software ImageJ. (G-H) MCF-7 cells were treated with or without 1 μM ADR for 2 h, followed by fractionating into extracts as described in Materials and Methods. Immunoblotting was conducted using the indicated antibodies(G). Quantitative results of the indicated signal are shown in H. S, cytoplasmic fraction; P, nucleoplasmic fraction; C, nuclease-resistant fraction of nucleosomes. (I-J) MCF-7 cells stably expressing WT or K767R MORC2 were treated with 1 μM ADR for 2 h, and fractionated into extracts as described in G. Immunoblotting was conducted using the indicated antibodies (I). Quantitative results of H3K9me3 signal are shown in J.