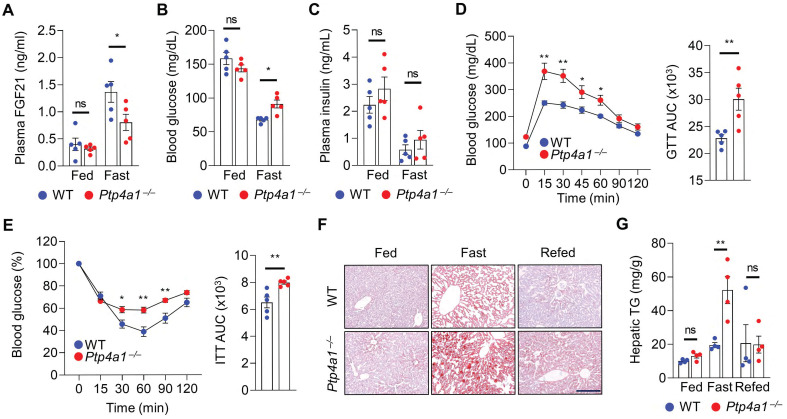
Figure 4.
Lacking PTP4A1 in mice increases blood glucose and NAFLD by the down-regulation of FGF21 expression in fasting conditions. (A) Plasma FGF21 levels in wild-type (WT) and Ptp4a1-/- mice on a normal chow (NC) diet in feeding and fasting conditions (n = 5). (B and C) The blood glucose levels (B) and plasma insulin levels (C) in WT and Ptp4a1-/- mice on an NC diet in feeding and fasting conditions (n = 5). (D) Glucose tolerance test (GTT) and the area under the curve (AUC) of GTT in WT and Ptp4a1-/- mice fed an NC diet (n = 5). (E) Insulin tolerance test (ITT) and the AUC of ITT in WT and Ptp4a1-/- mice fed an NC diet (n = 5). (F) The representative images for oil red O staining in the liver sections of WT and Ptp4a1-/- mice fed an NC diet in feeding, fasting, and refeeding conditions (n = 4). Scale bar, 200 μm. (G) Hepatic triglyceride (TG) of WT and Ptp4a1-/- mice fed an NC diet in feeding, fasting, and refeeding conditions (n = 4). Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, n.s., not significant (two-way ANOVA for A-C, D (left), E (left) and G; Mann-Whitney U test for D (right) and E (right)).