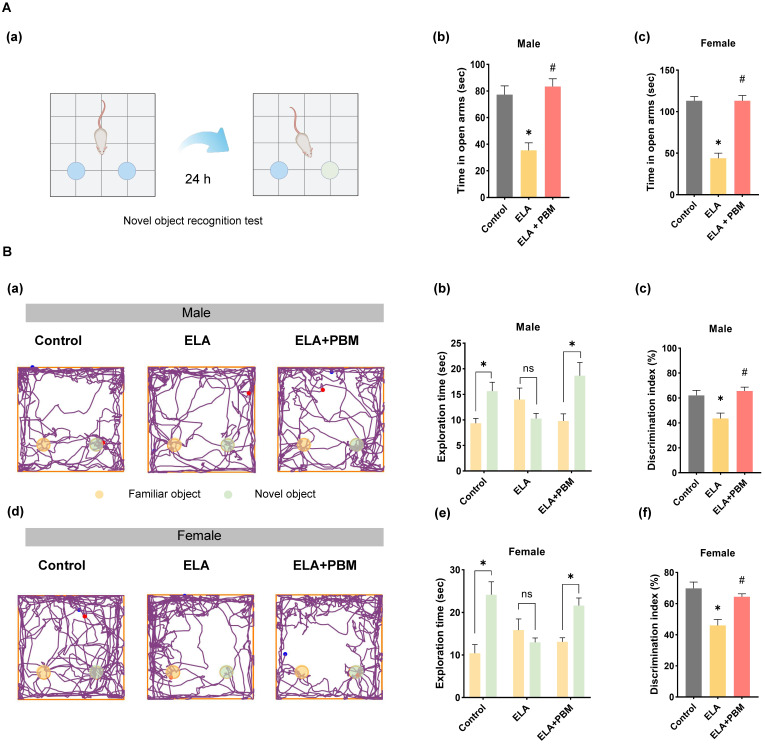
Figure 3.
Early PBM treatment prevents ELA-induced cognitive deficits and comorbidity. A (a) Schematic diagram of the novel object recognition test. The novel object recognition test was conducted to measure the recognition memory. A (b, c) The elevated plus maze text was performed to measure anxious-like behavior, PBM-treated ELA rats spent significantly more time in the open arms than their untreated counterparts. B (a, d) The representative tracking plots on the novel object recognition test. Between all groups, the time spent on each object and discrimination index was calculated and statistically compared (b-c, e-f). ELA rats spent significantly less time exploring the novel object, while early PBM treatment reserved these deficits. All data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 5-7). * P < 0.05 versus Control-group; # P < 0.05 versus ELA-group.