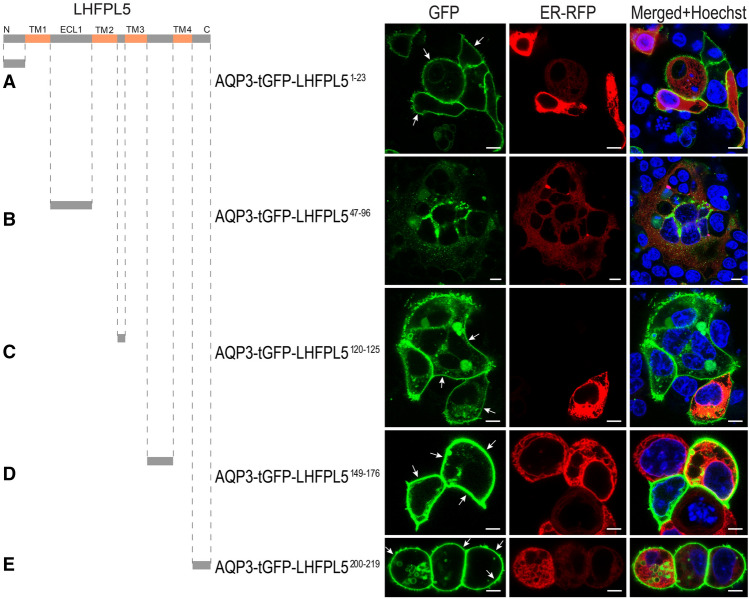
Figure 1.
AGR discerns the ability of LHFPL5 regions to halt trafficking to the PM. AGR-based method was used to examine whether any of intracellular and extracellular loops, as well as N- and C-termini of LHFPL5 have the ability to preclude any detectable reporter trafficking to the PM. (A) The N-terminus fragment of LHFPL5, comprising residues LHFPL51–23, does not preclude trafficking of the AGR system to the PM. When expressed in HEK293 cells, AQP3-tGFP-LHFPL51–23 exhibit robust PM localization (white arrows). (B) In contrast, extracellular loop 1, consisting of LHFPL547–96 fragment, halts any detectable trafficking to the PM. AQP3-tGFP-LHFPL51–23 expression shows an intracellular only labeling pattern. (C–E) AGR-based constructs containing the remaining intracellular loop 1, LHFPL5120–125 (C), extracellular loop 2, LHFPL5149–176 (D) or the C-terminus, LHFPL5200–219 (E) show PM labeling. Scale bars: 10 µm. ER was labeled with ER-red fluorescent protein (ER-RFP) in all figures.